来自今天的爱可可AI前沿推介
[CL] Binarized Neural Machine Translation
Y Zhang, A Garg, Y Cao, Ł Lew, B Ghorbani, Z Zhang, O Firat
[Cornell University & Google Research]
二值化神经机器翻译
要点:
-
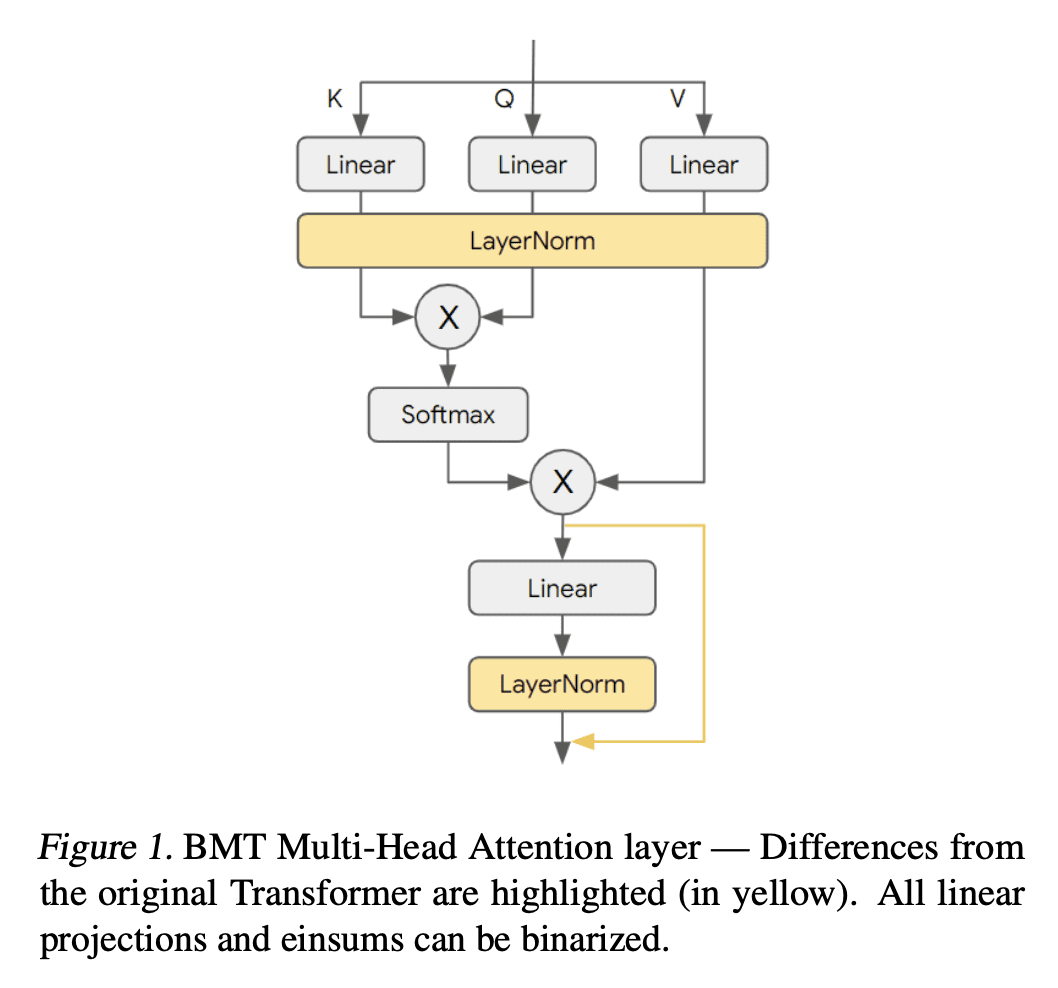
BMT 是机器翻译 Transformer 的一种新的二值化技术; -
BMT 通过利用额外的 LayerNorm 和残差连接来提高二值化质量,解决了使用 1bit 权重和激活时点积方差膨胀的问题; -
BMT 实现了与浮点模型相同的质量,同时模型大小比只用 1bit 权重的 Transformer 小16倍,但 1bit 激活会产生不同程度的质量下降; -
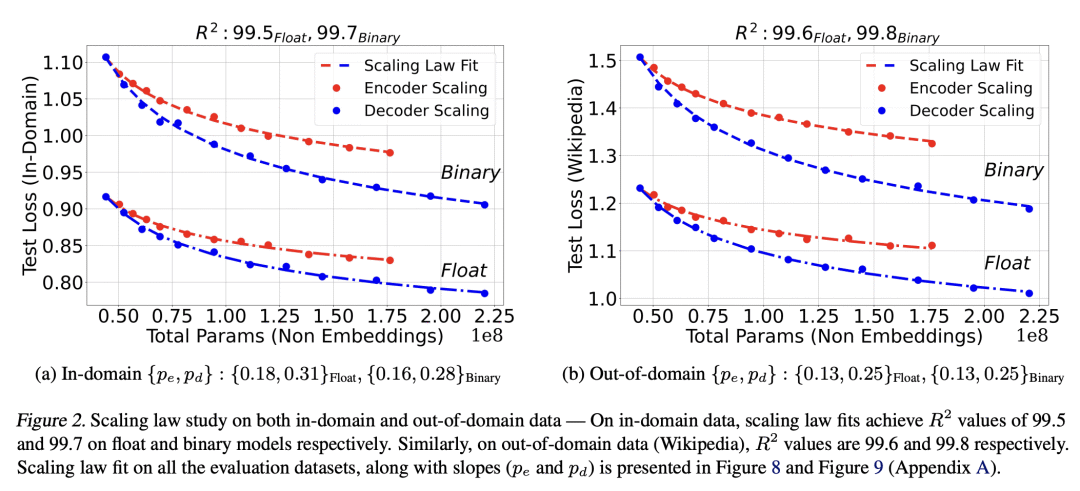
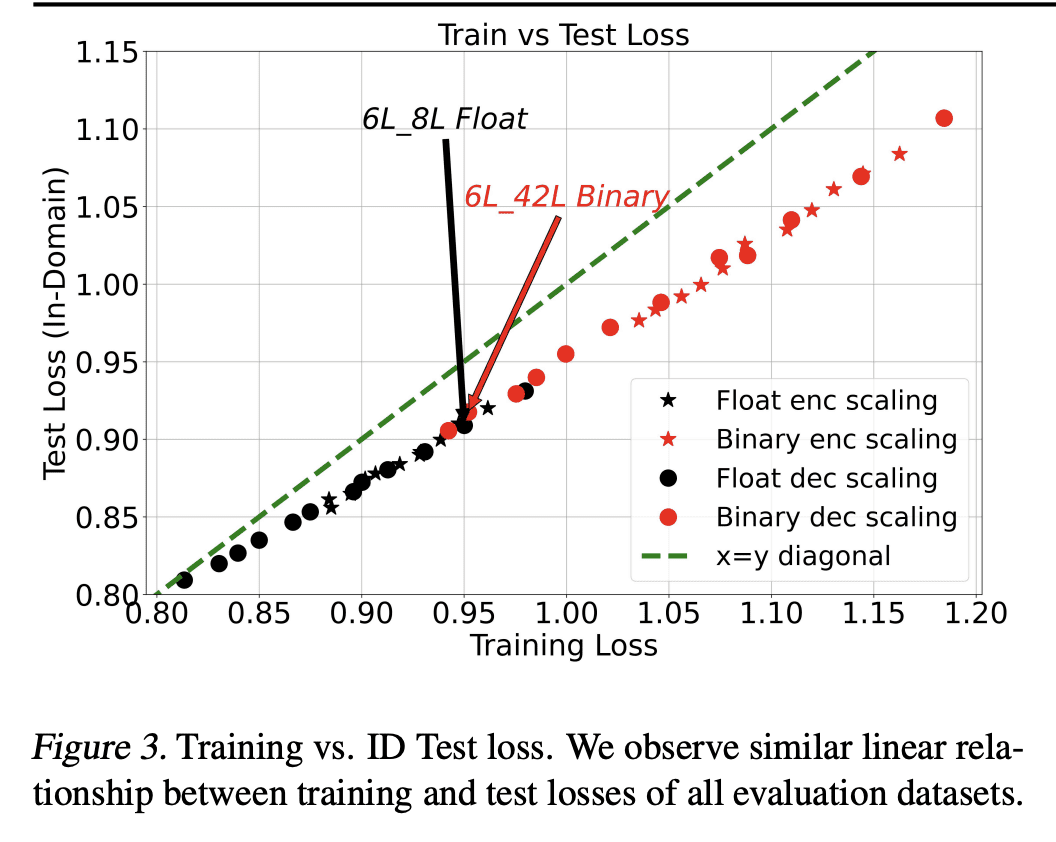
BMT在域内和域外的设置中,都有很好的扩展性和泛化性,二值化可以成为未来机器翻译模型服务的潜在替代技术。
一句话总结:
提出一种新的机器翻译中 Transformer 的二值化技术BMT,解决了使用 1bit 权重和激活时点积方差膨胀的问题,利用额外的 LayerNorm 和残差连接提高二值化质量,可以实现机器翻译的二值化,在保持翻译质量的同时减少模型的大小。
The rapid scaling of language models is motivating research using low-bitwidth quantization. In this work, we propose a novel binarization technique for Transformers applied to machine translation (BMT), the first of its kind. We identify and address the problem of inflated dot-product variance when using one-bit weights and activations. Specifically, BMT leverages additional LayerNorms and residual connections to improve binarization quality. Experiments on the WMT dataset show that a one-bit weight-only Transformer can achieve the same quality as a float one, while being 16x smaller in size. One-bit activations incur varying degrees of quality drop, but mitigated by the proposed architectural changes. We further conduct a scaling law study using production-scale translation datasets, which shows that one-bit weight Transformers scale and generalize well in both in-domain and out-of-domain settings. Implementation in JAX/Flax will be open sourced.
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.04907
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢