来自今天的爱可可AI前沿推介
[LG] Guiding Pretraining in Reinforcement Learning with Large Language Models
Y Du, O Watkins, Z Wang, C Colas, T Darrell, P Abbeel, A Gupta, J Andreas
[UC Berkeley & University of Washington & MIT]
基于大型语言模型指导强化学习预训练
要点:
-
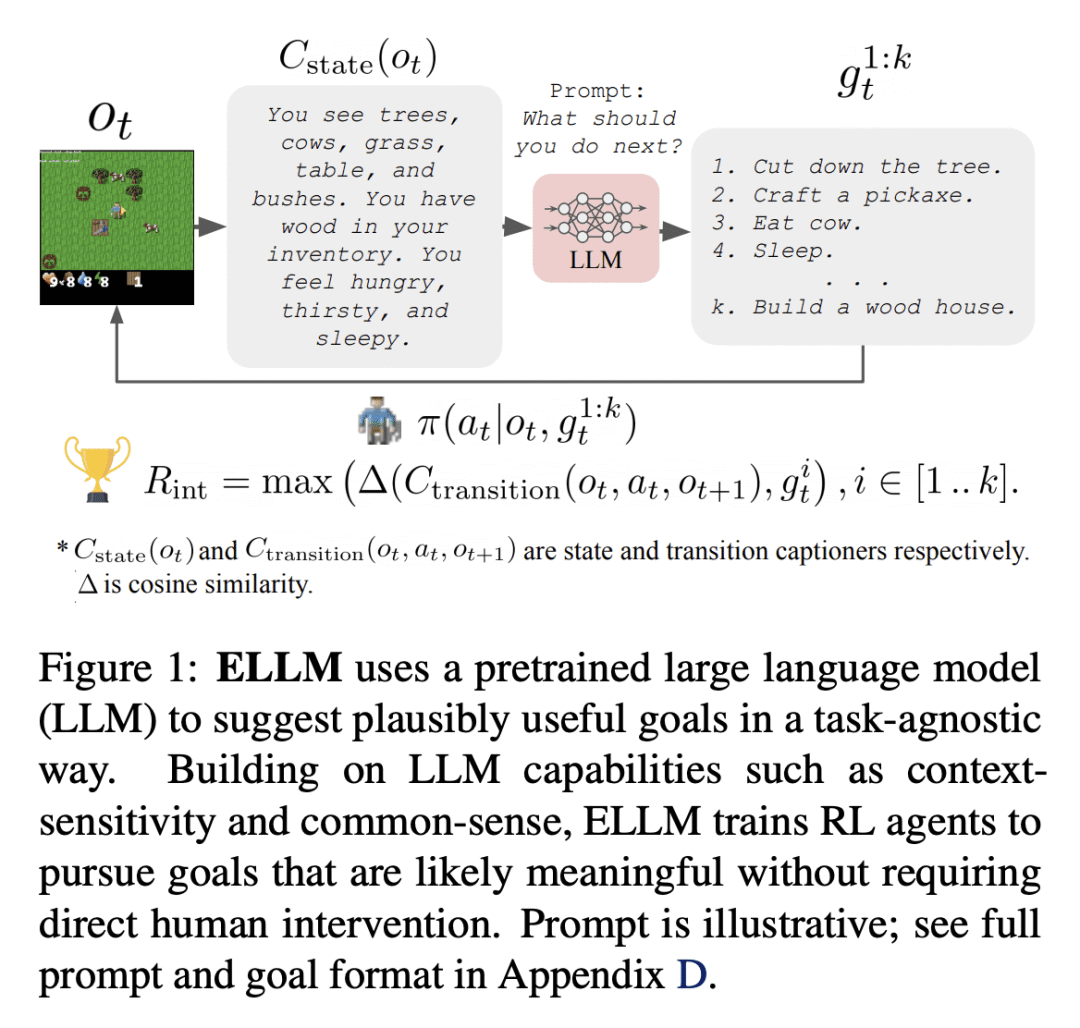
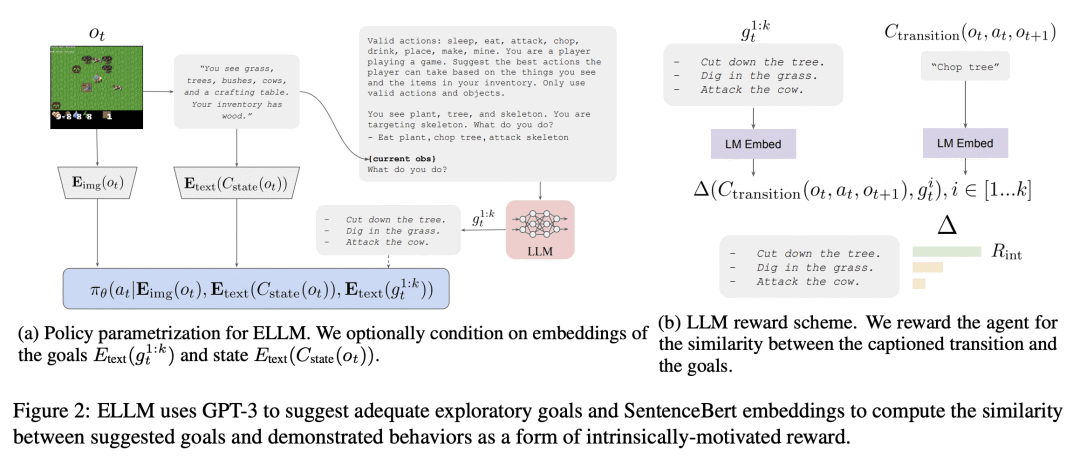
提出一种新的内在动机强化学习方法,ELLM,基于预训练的LLM来进行探索; -
ELLM 使探索偏向于常识性的和合理的有用行为; -
在预训练期间,ELLM 训练的智能体表现出对有用行为的更好覆盖,并且在下游任务中进行微调时,表现优于或相当于基线; -
然而,ELLM 在基于目标的探索空间很小的环境中,或者在状态信息没有自然编码为自然语言字符串的环境中,帮助不大。
一句话总结:
使用大型预训练语言模型可以引导强化学习智能体走向有用的和对人类有意义的行为。
Reinforcement learning algorithms typically struggle in the absence of a dense, well-shaped reward function. Intrinsically motivated exploration methods address this limitation by rewarding agents for visiting novel states or transitions, but these methods offer limited benefits in large environments where most discovered novelty is irrelevant for downstream tasks. We describe a method that uses background knowledge from text corpora to shape exploration. This method, called ELLM (Exploring with LLMs) rewards an agent for achieving goals suggested by a language model prompted with a description of the agent's current state. By leveraging large-scale language model pretraining, ELLM guides agents toward human-meaningful and plausibly useful behaviors without requiring a human in the loop. We evaluate ELLM in the Crafter game environment and the Housekeep robotic simulator, showing that ELLM-trained agents have better coverage of common-sense behaviors during pretraining and usually match or improve performance on a range of downstream tasks.
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.06692

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢