On the Planning Abilities of Large Language Models (A Critical Investigation with a Proposed Benchmark
K Valmeekam, S Sreedharan, M Marquez...
[Arizona State University & Colorado State University]
大型语言模型的规划能力
要点:
-
大型语言模型在常识性规划任务中生成和验证规划的能力是微不足道的,平均只有3%左右的成功率; -
LLM 生成的规划可以被健全的规划器迅速纠正,以保证其合理性; -
有 LLM 作为计划助手,展示了由人在回路产生的规划的准确性的适度改善; -
所开发的基准套件和评估工具可供研究界评估LLM的规划能力。
一句话总结:
大型语言模型(LLM)的自主规划能力有限,但可以为人或AI规划器提供启发式指导。
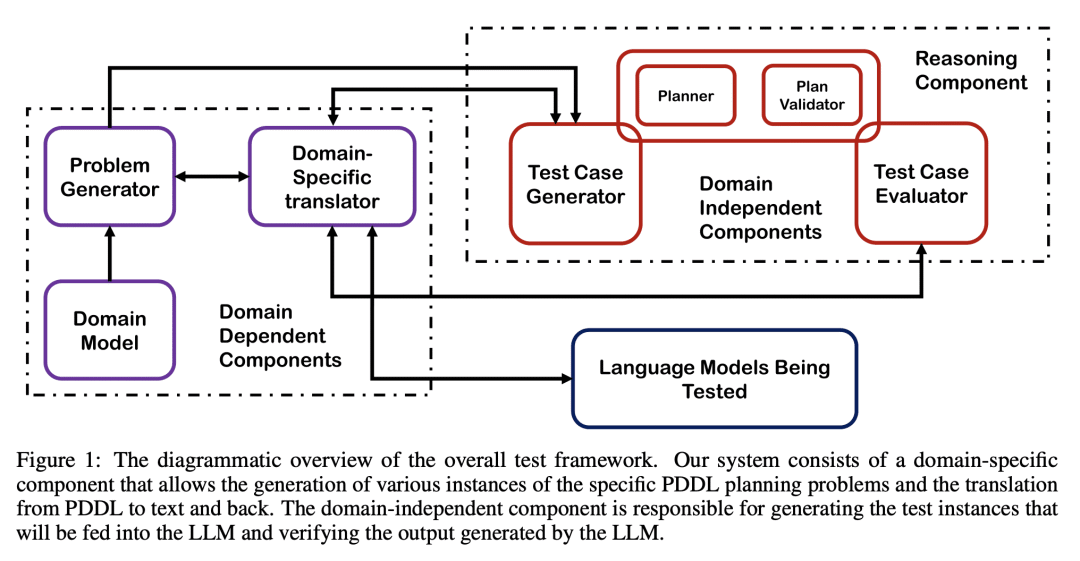
Intrigued by the claims of emergent reasoning capabilities in LLMs trained on general web corpora, in this paper, we set out to investigate their planning capabilities. We aim to evaluate (1) how good LLMs are by themselves in generating and validating simple plans in commonsense planning tasks (of the type that humans are generally quite good at) and (2) how good LLMs are in being a source of heuristic guidance for other agents--either AI planners or human planners--in their planning tasks. To investigate these questions in a systematic rather than anecdotal manner, we start by developing a benchmark suite based on the kinds of domains employed in the International Planning Competition. On this benchmark, we evaluate LLMs in three modes: autonomous, heuristic and human-in-the-loop. Our results show that LLM's ability to autonomously generate executable plans is quite meager, averaging only about 3% success rate. The heuristic and human-in-the-loop modes show slightly more promise. In addition to these results, we also make our benchmark and evaluation tools available to support investigations by research community.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.06706

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢