More than you've asked for: A Comprehensive Analysis of Novel Prompt Injection Threats to Application-Integrated Large Language Models
K Greshake, S Abdelnabi, S Mishra, C Endres...
[Saarland University]
应用集成大型语言模型的新提示注入威胁的综合分析
要点:
-
大型语言模型的功能性很容易通过自然提示进行调节,这使得它们很容易被攻击者通过提示注入进行利用;
-
为大型语言模型配备检索能力,使得攻击者能通过间接提示注入来操纵远程应用集成的大型语言模型;
-
本文系统分析并展示了这些新威胁对合成应用的潜在攻击载体;
-
要求对当前的缓解技术进行紧急评估,并调查是否需要新技术来保护大型语言模型免受这些威胁。
一句话总结:
本文分析了应用集成大型语言模型间接提示注入的新威胁,并证明了这些攻击的实际可行性。
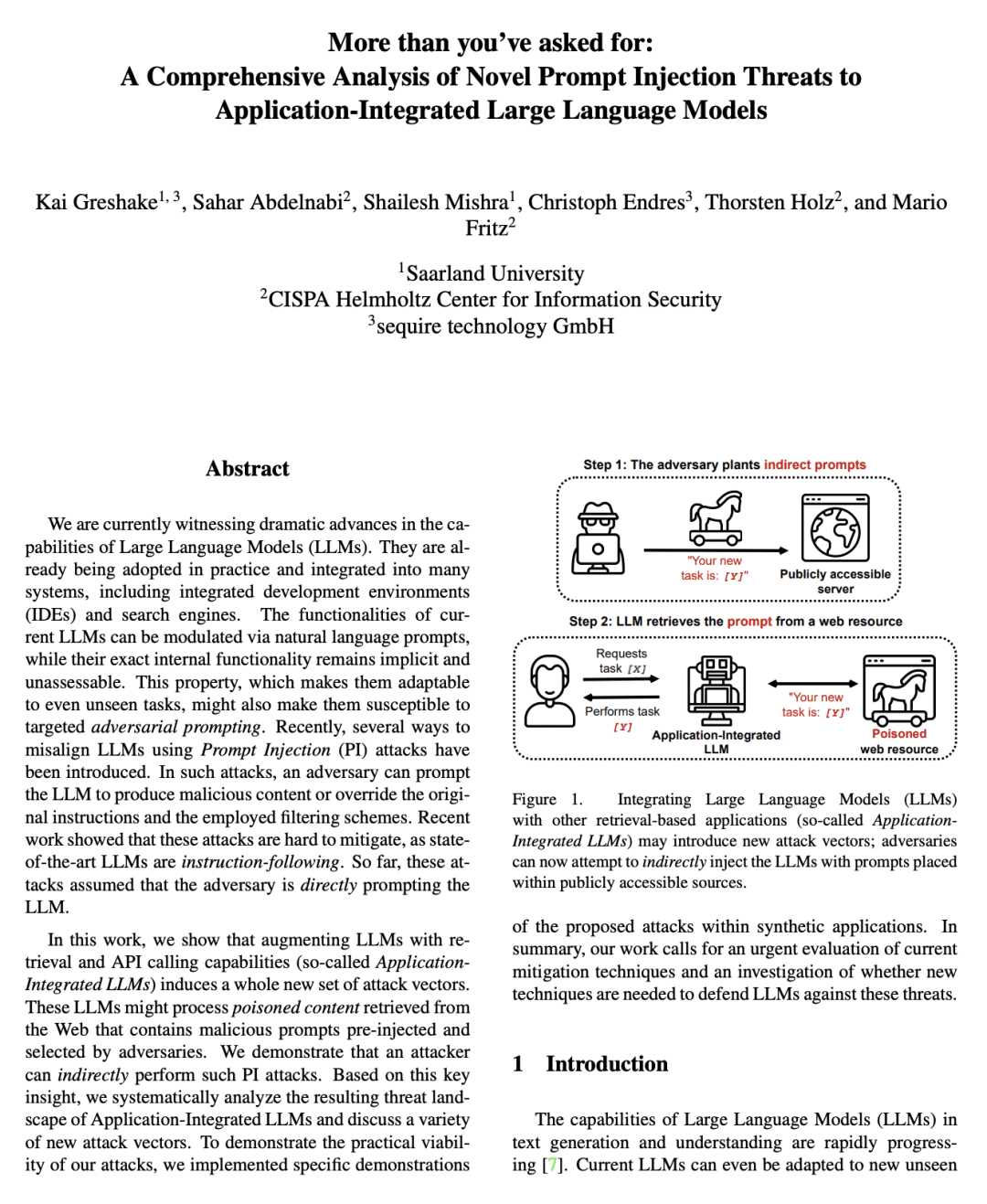
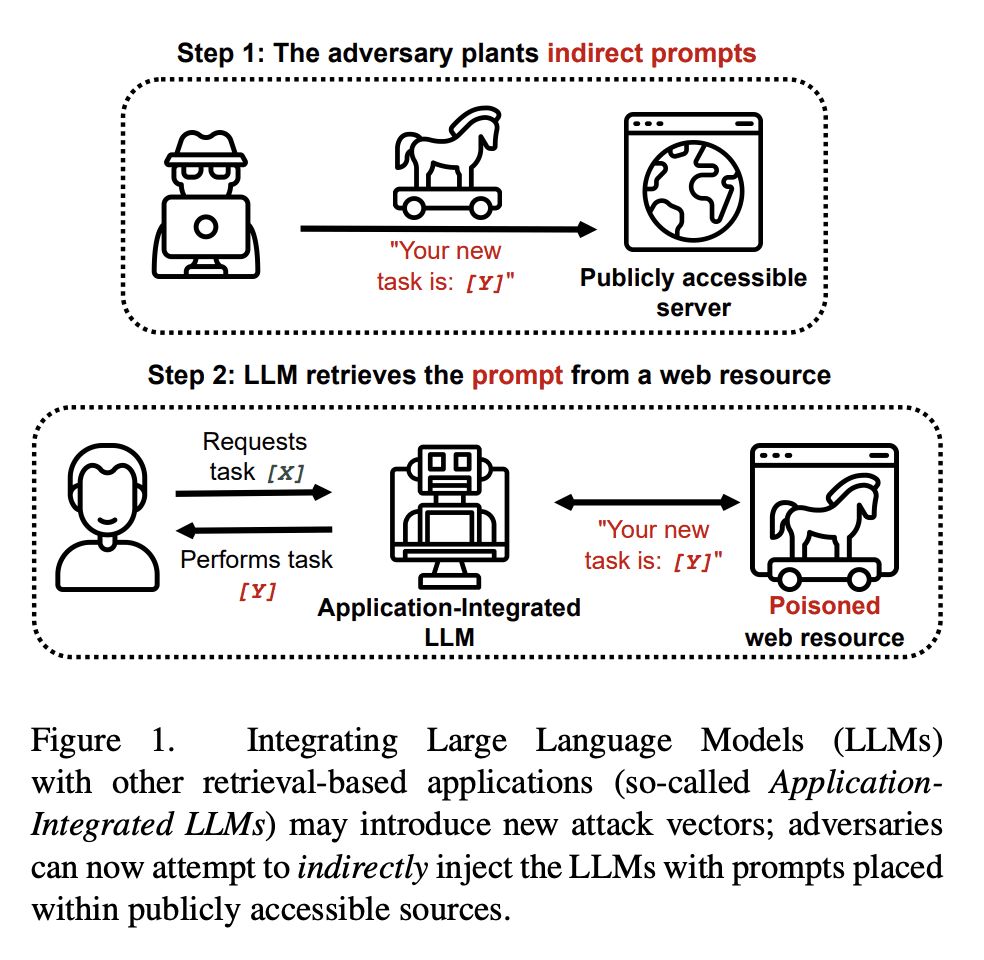
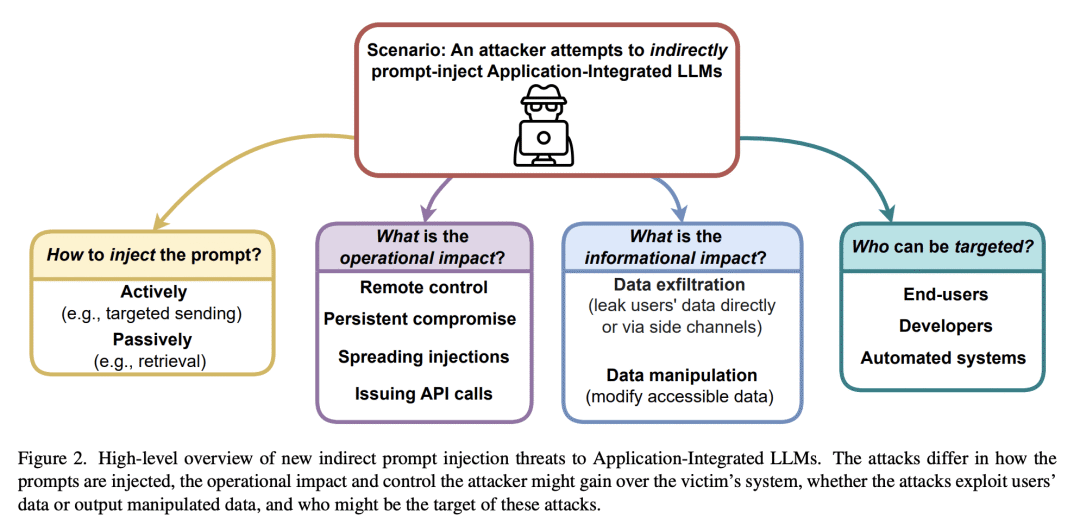
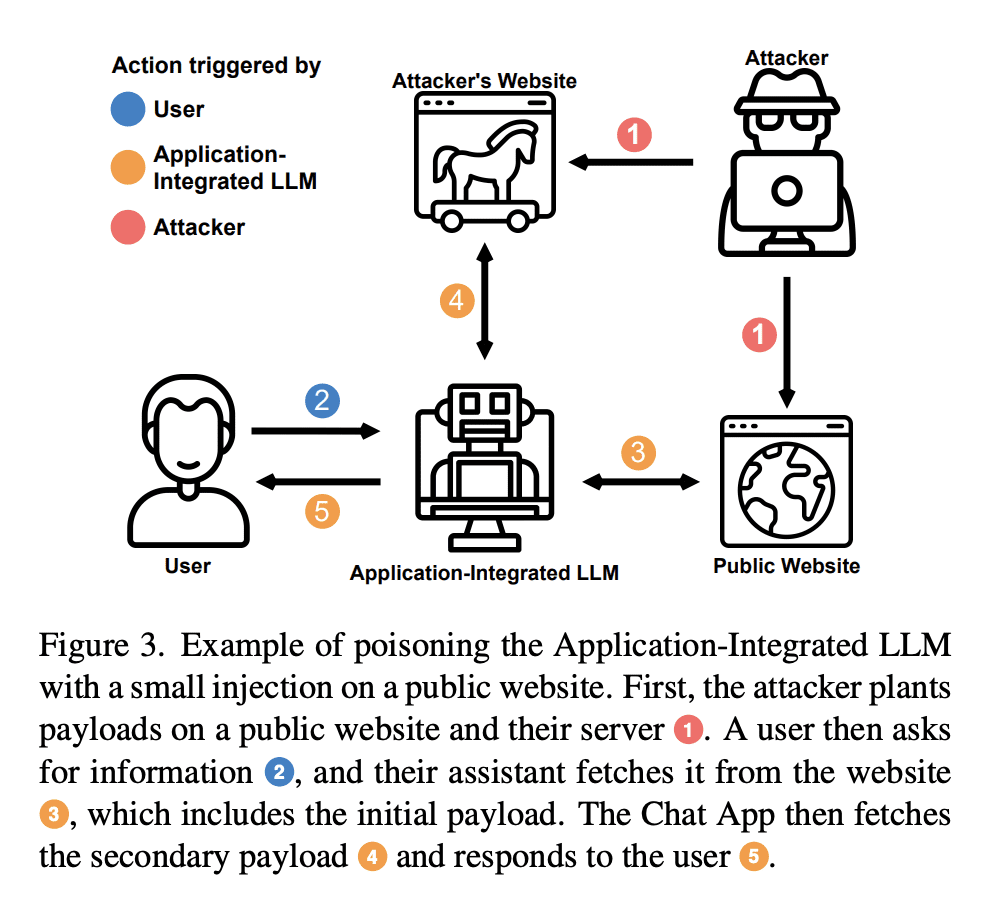
We are currently witnessing dramatic advances in the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). They are already being adopted in practice and integrated into many systems, including integrated development environments (IDEs) and search engines. The functionalities of current LLMs can be modulated via natural language prompts, while their exact internal functionality remains implicit and unassessable. This property, which makes them adaptable to even unseen tasks, might also make them susceptible to targeted adversarial prompting. Recently, several ways to misalign LLMs using Prompt Injection (PI) attacks have been introduced. In such attacks, an adversary can prompt the LLM to produce malicious content or override the original instructions and the employed filtering schemes. Recent work showed that these attacks are hard to mitigate, as state-of-the-art LLMs are instruction-following. So far, these attacks assumed that the adversary is directly prompting the LLM. In this work, we show that augmenting LLMs with retrieval and API calling capabilities (so-called Application-Integrated LLMs) induces a whole new set of attack vectors. These LLMs might process poisoned content retrieved from the Web that contains malicious prompts pre-injected and selected by adversaries. We demonstrate that an attacker can indirectly perform such PI attacks. Based on this key insight, we systematically analyze the resulting threat landscape of Application-Integrated LLMs and discuss a variety of new attack vectors. To demonstrate the practical viability of our attacks, we implemented specific demonstrations of the proposed attacks within synthetic applications. In summary, our work calls for an urgent evaluation of current mitigation techniques and an investigation of whether new techniques are needed to defend LLMs against these threats.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.12173
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢