Zero-Shot Information Extraction via Chatting with ChatGPT
Xiang Wei, Xingyu Cui, Ning Cheng, Xiaobin Wang, Xin Zhang, Shen Huang, Pengjun Xie, Jinan Xu, Yufeng Chen, Meishan Zhang, Yong Jiang, Wenjuan Han
Beijing Jiaotong University & DAMO Academy
通过ChatGPT聊天提取零样本信息
要点:
1.零镜头信息提取(IE)旨在从未注释的文本中构建IE系统。由于几乎不需要人为干预,这是一项具有挑战性的工作。具有挑战性但值得一试的零镜头IE减少了数据标记所需的时间和精力。
2.最近在大型语言模型(LLM,例如GPT-3、ChatGPT)上的研究表明,在零镜头设置下的性能很有希望,因此激励我们探索基于提示的方法。
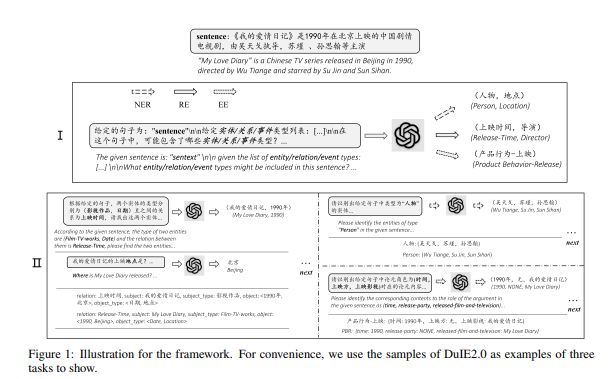
3.在这项工作中,我们询问是否可以通过直接提示LLM来构建强IE模型。具体地说,将零镜头IE任务转换为具有两阶段框架(ChatIE)的多回合问答问题。
4.借助ChatGPT的强大功能,文章在三个IE任务上广泛评估了我们的框架:实体关系三重提取、命名实体识别和事件提取。
一句话总结:
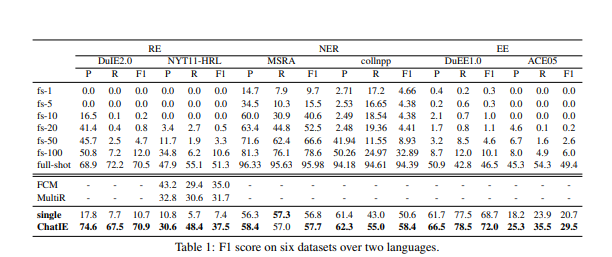
在两种语言的六个数据集上的经验结果表明,ChatIE取得了令人印象深刻的性能,甚至在几个数据集上超过了一些完整的模型(例如,NYT11-HRL)。这项工作将有助于在有限的资源下构建IE模型。[机器翻译+人工校对]
Zero-shot information extraction (IE) aims to build IE systems from the unannotated text. It is challenging due to involving little human intervention. Challenging but worthwhile, zero-shot IE reduces the time and effort that data labeling takes. Recent efforts on large language models (LLMs, e.g., GPT-3, ChatGPT) show promising performance on zero-shot settings, thus inspiring us to explore prompt-based methods. In this work, we ask whether strong IE models can be constructed by directly prompting LLMs. Specifically, we transform the zero-shot IE task into a multi-turn question-answering problem with a two-stage framework (ChatIE). With the power of ChatGPT, we extensively evaluate our framework on three IE tasks: entity-relation triple extract, named entity recognition, and event extraction. Empirical results on six datasets across two languages show that ChatIE achieves impressive performance and even surpasses some full-shot models on several datasets (e.g., NYT11-HRL). We believe that our work could shed light on building IE models with limited resources.
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2302.10205.pdf

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢