ELITE: Encoding Visual Concepts into Textual Embeddings for Customized Text-to-Image Generation
Yuxiang Wei, Yabo Zhang, Zhilong Ji, Jinfeng Bai, Lei Zhang, Wangmeng Zuo
Harbin Institute of Technology & The Hong Kong Polytechnic University & Tomorrow Advancing Life
ELITE:将视觉概念编码为文本嵌入以生成定制的文本到图像
要点:
1.尽管在想象创造方面具有前所未有的能力,但大型文本到图像模型有望进一步表达定制概念。 现有作品通常以基于优化的方式学习这些概念,但会带来过多的计算或内存负担。
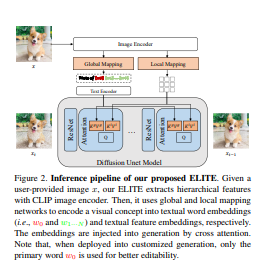
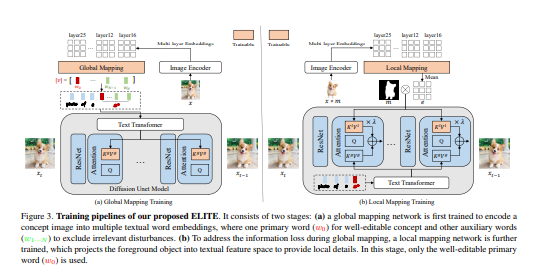
2.在本文中,提出了一种基于学习的编码器,用于快速准确的概念定制,它由全局和局部映射网络组成。 具体来说,全局映射网络将给定图像的层次特征分别投射到文本词嵌入空间中的多个“新”词,即一个主词用于可编辑的概念和其他辅助词以排除不相关的干扰( 例如,背景)。 同时,本地映射网络将编码的补丁特征注入交叉注意层以提供省略的细节,而不会牺牲主要概念的可编辑性。
一句话总结:
将该方法与先前基于优化的方法在各种用户定义的概念上进行比较,并证明该方法能够以更快的编码过程实现更高保真度的反演和稳健的可编辑性。 代码将在 https://github.com/csyxwei/ELITE 上公开。
Despite unprecedented ability in imaginary creation, large text-to-image models are further expected to express customized concepts. Existing works generally learn such concepts in an optimization-based manner, yet bringing excessive computation or memory burden. In this paper, we instead propose a learning-based encoder for fast and accurate concept customization, which consists of global and local mapping networks. In specific, the global mapping network separately projects the hierarchical features of a given image into multiple ``new'' words in the textual word embedding space, i.e., one primary word for well-editable concept and other auxiliary words to exclude irrelevant disturbances (e.g., background). In the meantime, a local mapping network injects the encoded patch features into cross attention layers to provide omitted details, without sacrificing the editability of primary concepts. We compare our method with prior optimization-based approaches on a variety of user-defined concepts, and demonstrate that our method enables more high-fidelity inversion and robust editability with a significantly faster encoding process. Our code will be publicly available at https://github.com/csyxwei/ELITE.
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2302.13848.pdf


内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢