LODE: Locally Conditioned Eikonal Implicit Scene Completion from Sparse LiDAR
Pengfei Li, Ruowen Zhao, Yongliang Shi, Hao Zhao, Jirui Yuan, Guyue Zhou, Ya-Qin Zhang
Tsinghua University & University of Chinese Academy of Science
LODE:来自稀疏 LiDAR 的局部条件 Eikonal 隐式场景完成
要点:
1.场景补全是指从复杂 3D 场景的不完整感知中获得密集的场景表示。 这有助于机器人在自动驾驶等场景中检测多尺度障碍物并分析物体遮挡。 最近的进展表明,隐式表示学习可以用于连续的场景完成,并通过像 Eikonal 方程这样的物理约束来实现。 然而,以前的 Eikonal 补全方法仅在数十个网格的水密网格上展示结果。 对于数千个场景规模的开放大场景的非水密 LiDAR 点云,它们都没有成功完成。
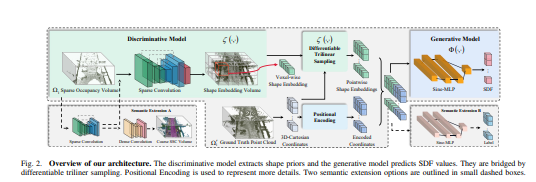
2.在本文中,提出了一种新的 Eikonal 公式,它以局部形状先验的隐式表示为条件,用作密集边界值约束,并证明它适用于 SemanticKITTI 和 SemanticPOSS。 它也可以扩展到语义 Eikonal 场景完成,只需对网络架构进行少量修改。
- 开发了一种局部条件化的Eikonal 隐式场景完成公式,该公式将学习到的形状先验作为密集边界值约束。
- 将公式应用于道路场景理解,导致第一个在不知道自由空间中的SDF 值的情况下使用Eikonal 隐式道路场景补全方法。
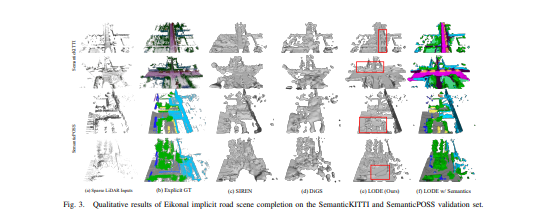
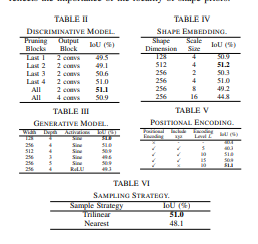
- 在 SemanticKITTI 和 SemanticPOSS 上取得了最先进的完成结果,比最好的 Eikonal 完成结果高出 +19.5% 和 +8.2% IoU。 代码、数据和模型将被发布。
一句话总结:
通过广泛的定量和定性结果,证明了现有 Eikonal 方法的优点和缺点,这自然会导致新的局部条件公式。 值得注意的是,在 SemanticKITTI 上将 IoU 从 31.7% 提高到 51.2%,在 SemanticPOSS 上从 40.5% 提高到 48.7%。 广泛地消融了我们的方法,并证明了所提出的公式对广泛的实现超参数具有鲁棒性。 代码和模型可在 https://github.com/AIR-DISCOVER/LODE 上公开获得。[机器翻译+人工校对]
Scene completion refers to obtaining dense scene representation from an incomplete perception of complex 3D scenes. This helps robots detect multi-scale obstacles and analyse object occlusions in scenarios such as autonomous driving. Recent advances show that implicit representation learning can be leveraged for continuous scene completion and achieved through physical constraints like Eikonal equations. However, former Eikonal completion methods only demonstrate results on watertight meshes at a scale of tens of meshes. None of them are successfully done for non-watertight LiDAR point clouds of open large scenes at a scale of thousands of scenes. In this paper, we propose a novel Eikonal formulation that conditions the implicit representation on localized shape priors which function as dense boundary value constraints, and demonstrate it works on SemanticKITTI and SemanticPOSS. It can also be extended to semantic Eikonal scene completion with only small modifications to the network architecture. With extensive quantitative and qualitative results, we demonstrate the benefits and drawbacks of existing Eikonal methods, which naturally leads to the new locally conditioned formulation. Notably, we improve IoU from 31.7% to 51.2% on SemanticKITTI and from 40.5% to 48.7% on SemanticPOSS. We extensively ablate our methods and demonstrate that the proposed formulation is robust to a wide spectrum of implementation hyper-parameters. Codes and models are publicly available at https://github.com/AIR-DISCOVER/LODE
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2302.14052.pdf

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢