Knowledge-enhanced Pre-training for Auto-diagnosis of Chest Radiology Images
Xiaoman Zhang, Chaoyi Wu, Ya Zhang, Yanfeng Wang, Weidi Xie
[Shanghai Jiao Tong University & Shanghai AI Laboratory]
胸部放射学图像自动诊断的知识增强预训练
要点:
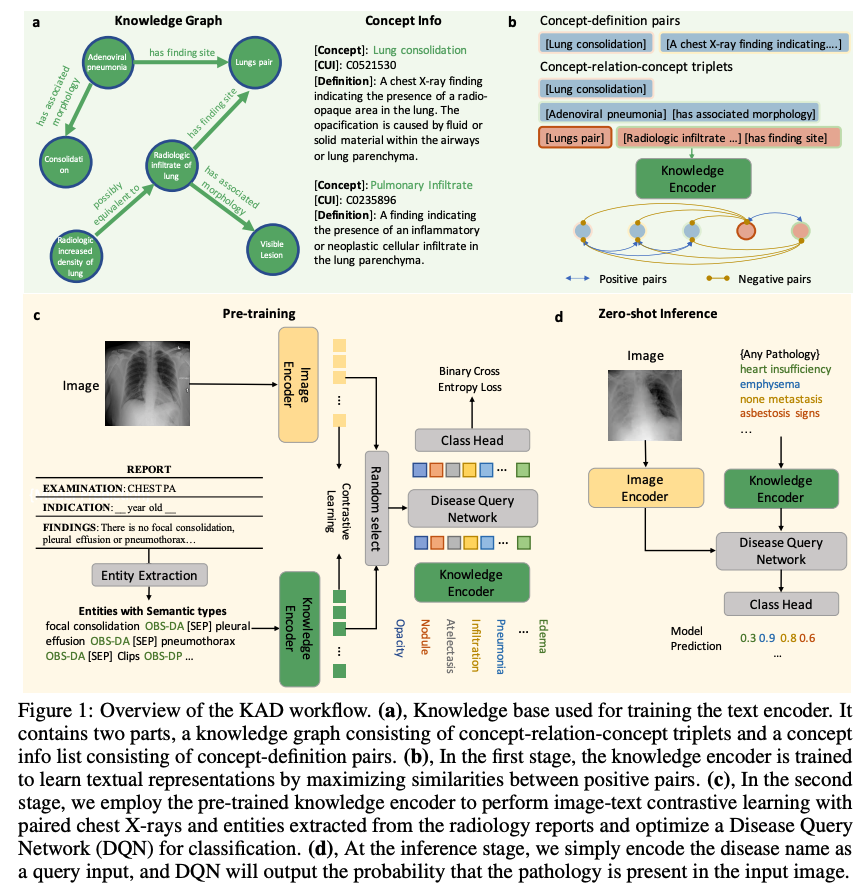
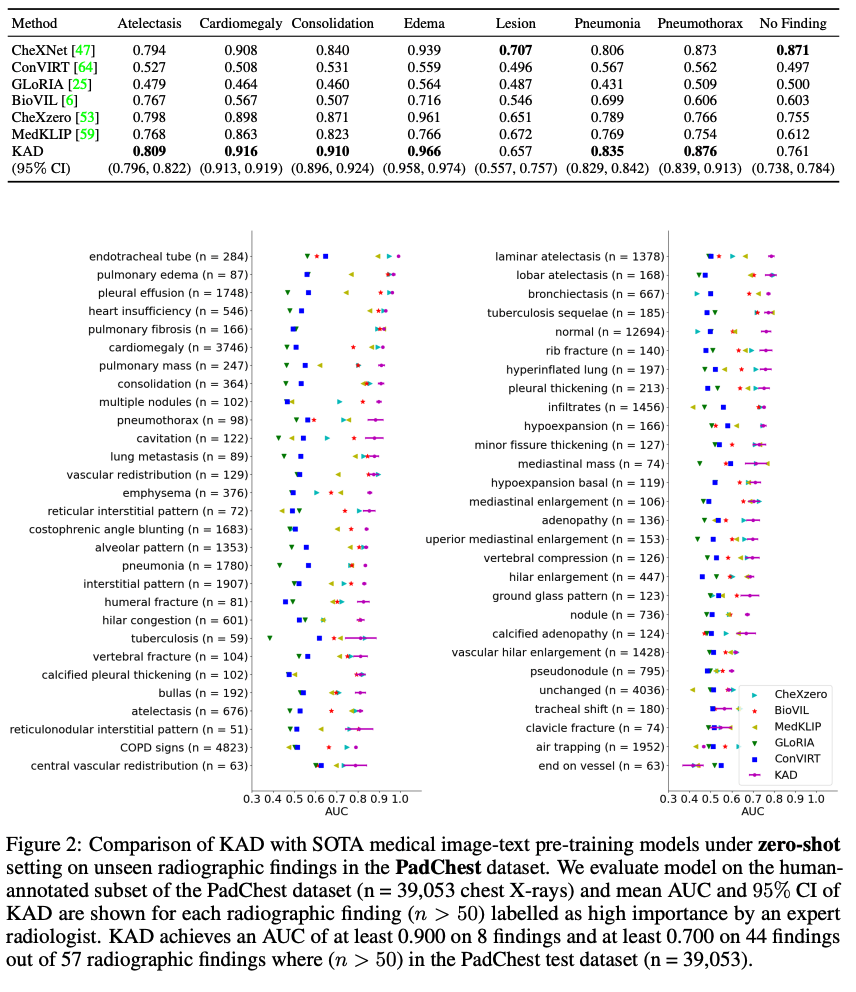
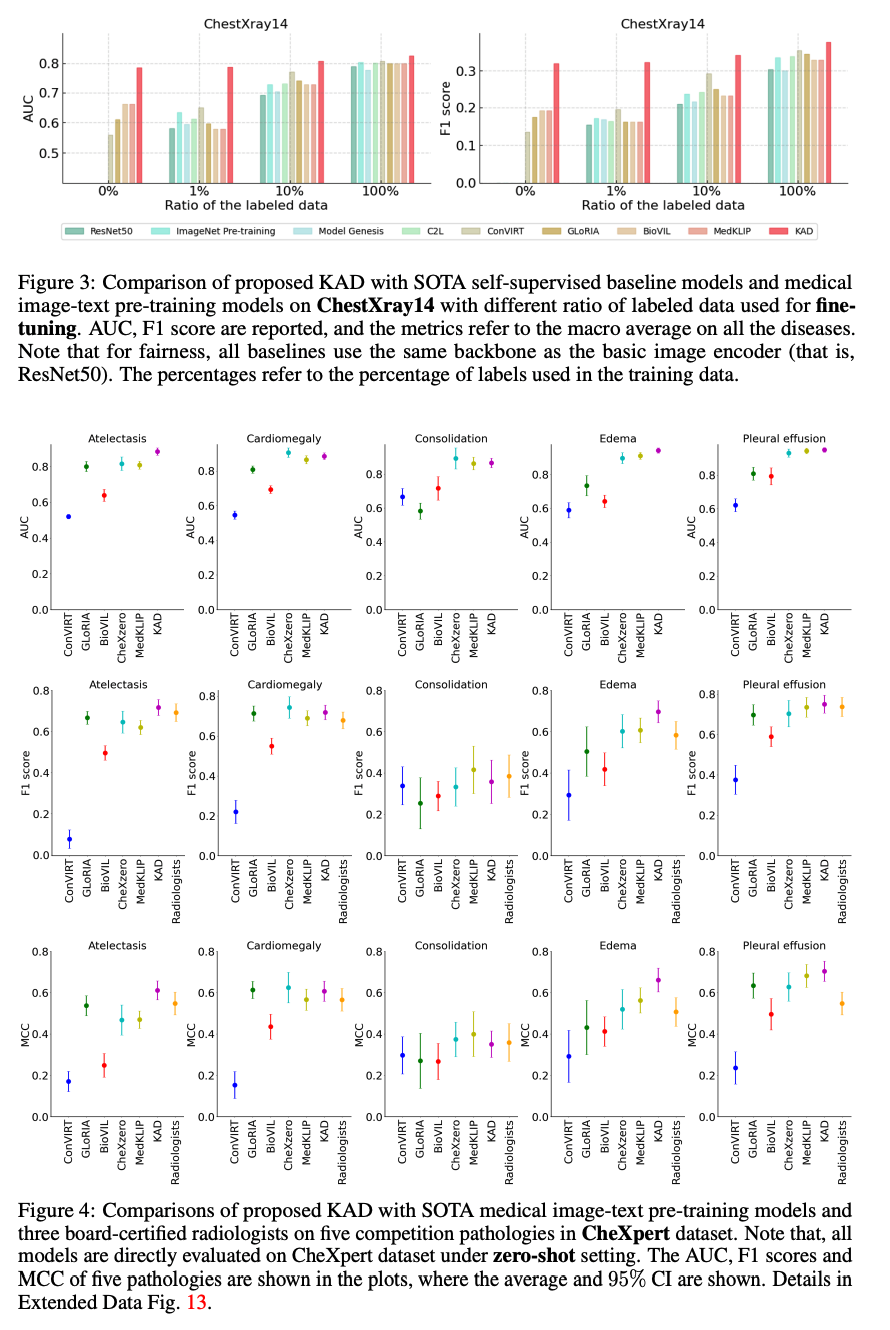
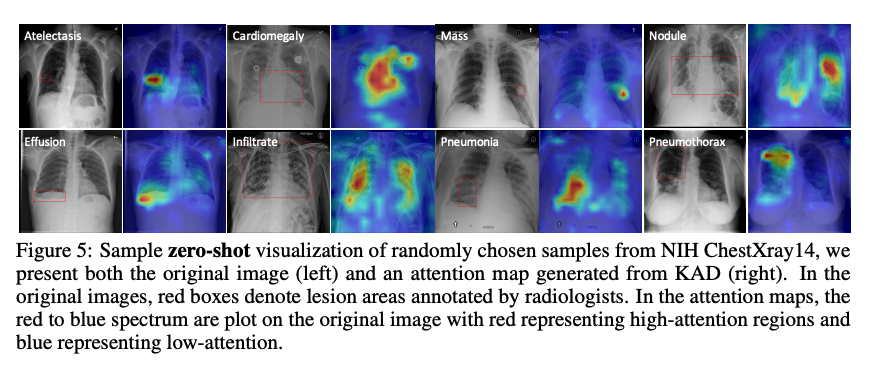
1、尽管在自然语言理解和视觉识别方面,基于大规模数据预训练的多模态基础模型取得了成功,但由于医学任务的细粒度识别性质,对领域知识的要求很高,因此其在医学和临床领域的对应模型仍处于初步阶段。2、本文提出了一种用于胸部X射线图像自动诊断的知识增强视觉语言预训练方法。该算法名为知识增强自动诊断(KAD),首先基于现有的医学知识图训练知识编码器,即学习医学概念之间的定义和关系的神经嵌入,然后利用预先训练的知识编码器来指导配对胸部X光片和放射学报告的视觉表示学习。在三个外部X射线数据集上通过实验验证了KAD的有效性。
一句话总结:
KAD的零射表现不仅可与完全监督的模型相比,而且首次优于三位(五分之三)具有统计学意义的病理学专家的平均水平。当少数镜头注释可用时,KAD在微调设置方面也超越了所有现有方法,展示了在不同临床场景中应用的潜力。
Despite of the success of multi-modal foundation models pre-trained on large-scale data in natural language understanding and vision recognition, its counterpart in medical and clinical domains remains preliminary, due to the fine-grained recognition nature of the medical tasks with high demands on domain knowledge. Here, we propose a knowledge-enhanced vision-language pre-training approach for auto-diagnosis on chest X-ray images. The algorithm, named Knowledge-enhanced Auto Diagnosis~(KAD), first trains a knowledge encoder based on an existing medical knowledge graph, i.e., learning neural embeddings of the definitions and relationships between medical concepts and then leverages the pre-trained knowledge encoder to guide the visual representation learning with paired chest X-rays and radiology reports. We experimentally validate KAD's effectiveness on three external X-ray datasets. The zero-shot performance of KAD is not only comparable to that of the fully-supervised models but also, for the first time, superior to the average of three expert radiologists for three (out of five) pathologies with statistical significance. When the few-shot annotation is available, KAD also surpasses all existing approaches in finetuning settings, demonstrating the potential for application in different clinical scenarios.
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2302.14042.pdf

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢