Chameleon: Plug-and-Play Compositional Reasoning with Large Language Models
提出名为“Chameleon”的即插即用组合推理框架,可增强大型语言模型(LLM)以解决其固有限制,帮助应对各种推理任务。Chameleon能合成程序以组合各种工具,包括LLM模型、现成的视觉模型、网络搜索引擎、Python函数和基于规则的模块,以满足用户的兴趣。在LLM作为自然语言规划器的基础上构建,Chameleon可以推断出适当的一系列工具来生成最终的响应。本研究在两个任务中展示了Chameleon的自适应性和有效性。
关于作者: 主要作者包括Pan Lu、Baolin Peng、Hao Cheng、Michel Galley、Kai-Wei Chang、Ying Nian Wu和Song-Chun Zhu。他们分别来自于多个机构,包括加州大学洛杉矶分校、微软研究院和加州理工学院等。他们之前的代表作包括“Neural Module Networks”和“Visual Genome”。
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.09842
-
动机:大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理的各种任务中取得了显著的进展,但仍面临各种固有限制,如无法访问最新信息、利用外部工具或进行精确的数学推理,本文旨在应对这些挑战。
-
方法:开发了一个插拔式组合推理框架,Chameleon,有效利用大型语言模型来解决它们固有的限制,并应对各种推理任务。成功整合了各种工具,包括LLM、现成的视觉模型、网络搜索引擎、Python函数和基于规则的模块,以构建一个多功能、可自适应的人工智能系统来回答现实世界的查询。
-
优势:在两个不同的基准测试中展示了该框架的自适应性和有效性,分别是ScienceQA和TabMWP,显著提升了现有的少样本和最先进模型的准确性。Chameleon展示了它在各种领域解决实际查询的潜力。
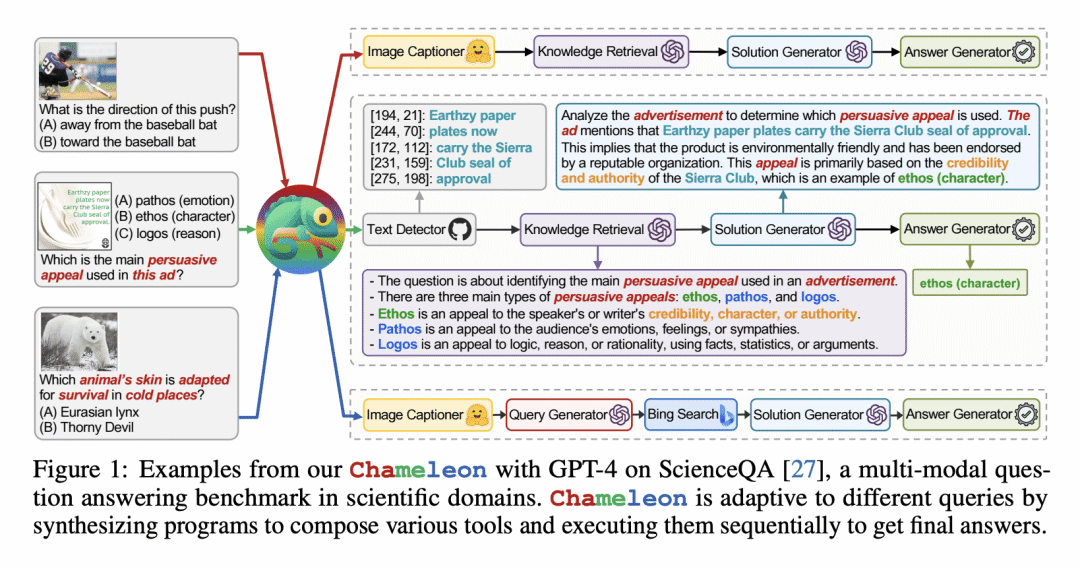
解决问题: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(LLMs)在获取最新信息、利用外部工具或进行精确数学推理等方面所面临的固有局限性,提出了Chameleon,一个插拔式的组合推理框架,旨在增强LLMs以应对这些挑战。
关键思路: Chameleon是一个插拔式的组合推理框架,可以合成程序以组合各种工具,包括LLM模型、现成的视觉模型、网络搜索引擎、Python函数和面向用户兴趣的基于规则的模块。基于LLM作为自然语言规划器,Chameleon推断出合适的工具序列以生成最终响应。Chameleon的亮点在于它增强了LLMs的能力,使其能够灵活适应不同任务,并在两个任务(ScienceQA和TabMWP)上展示了其适应性和有效性。相比当前领域的研究状况,Chameleon的思路在于增强LLMs的能力,使其能够更好地处理不同任务。
其他亮点: 该论文在ScienceQA和TabMWP两个任务上展示了Chameleon的适应性和有效性,使用GPT-4作为底层LLM,Chameleon在TabMWP上实现了98.78%的总体准确率,比现有技术水平提高了17.8%。此外,该论文还发现,使用GPT-4作为规划器能够更一致和理性地选择工具,并能够根据指令推断出潜在的约束条件,相比于其他LLMs如ChatGPT。
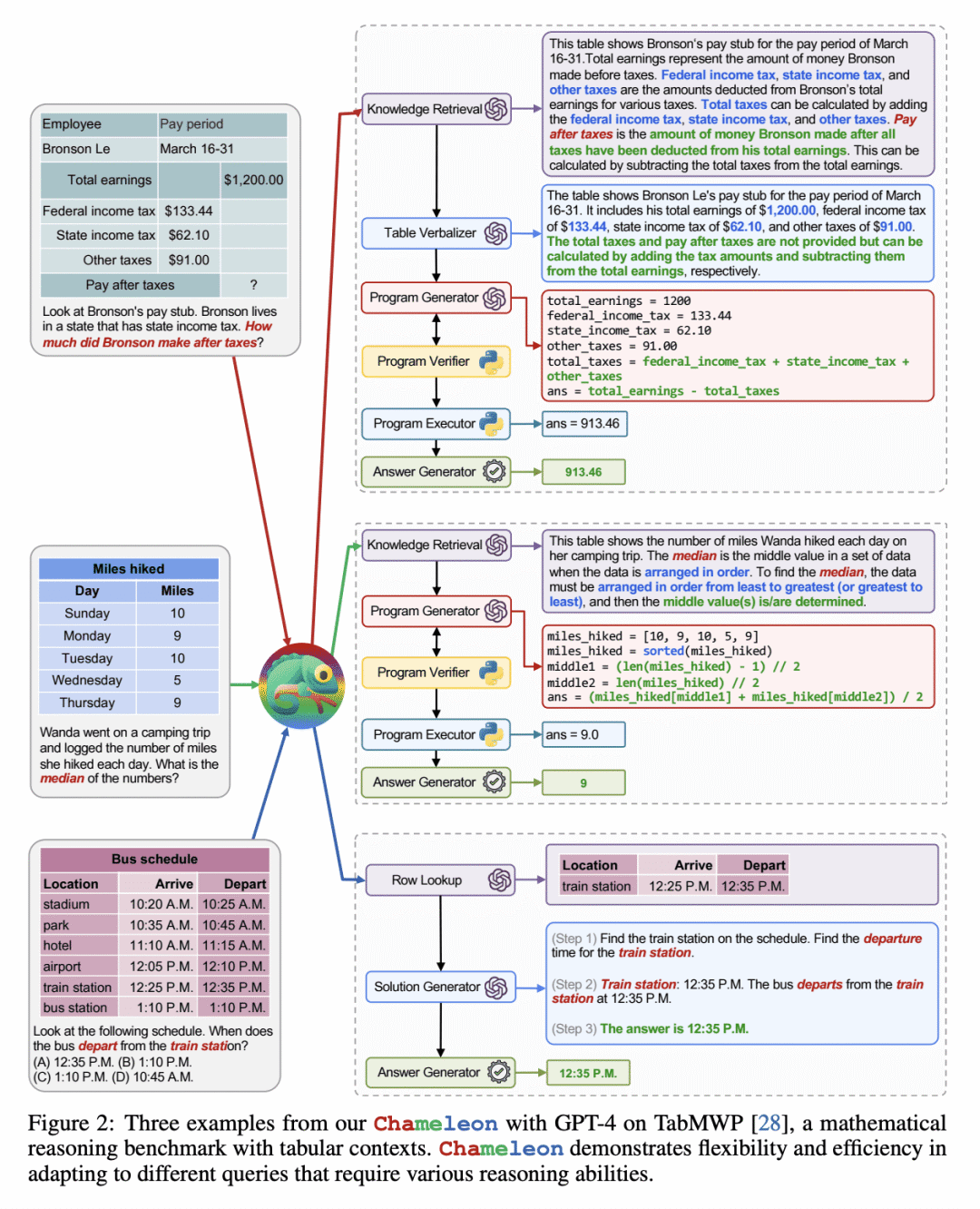
相关研究: 近期的相关研究包括:
- “Plug and Play Language Models: A Simple Approach to Controlled Text Generation”,作者包括Aditya Mogadala、Yi Tay、Dara Bahri等,来自于谷歌、新加坡国立大学等机构。
- “Plug and Play Super-Resolution for Arbitrary Size, Scale, and Noise Distributions”,作者包括Nikhil Suresh、Soheil Esmaeilzadeh等,来自于加州大学伯克利分校等机构。
论文摘要:本文介绍了一种名为“Chameleon”的插拔式组合推理框架,可增强大型语言模型(LLM)以帮助解决其固有的限制,如无法访问最新信息、利用外部工具或执行精确的数学推理。Chameleon综合各种工具,包括LLM模型、现成的视觉模型、网络搜索引擎、Python函数和基于规则的模块,以满足用户的个性化需求。Chameleon基于LLM作为自然语言规划器,推断出适当的工具序列以生成最终响应。作者在ScienceQA和TabMWP两个任务上展示了Chameleon的适应性和有效性。使用GPT-4作为底层LLM,Chameleon在ScienceQA上达到了86.54%的准确率,在TabMWP上实现了98.78%的整体准确率,比现有技术领先17.8%。进一步的研究表明,相比于ChatGPT等其他LLM,使用GPT-4作为规划器具有更一致和合理的工具选择,并能推断出可能的约束条件。
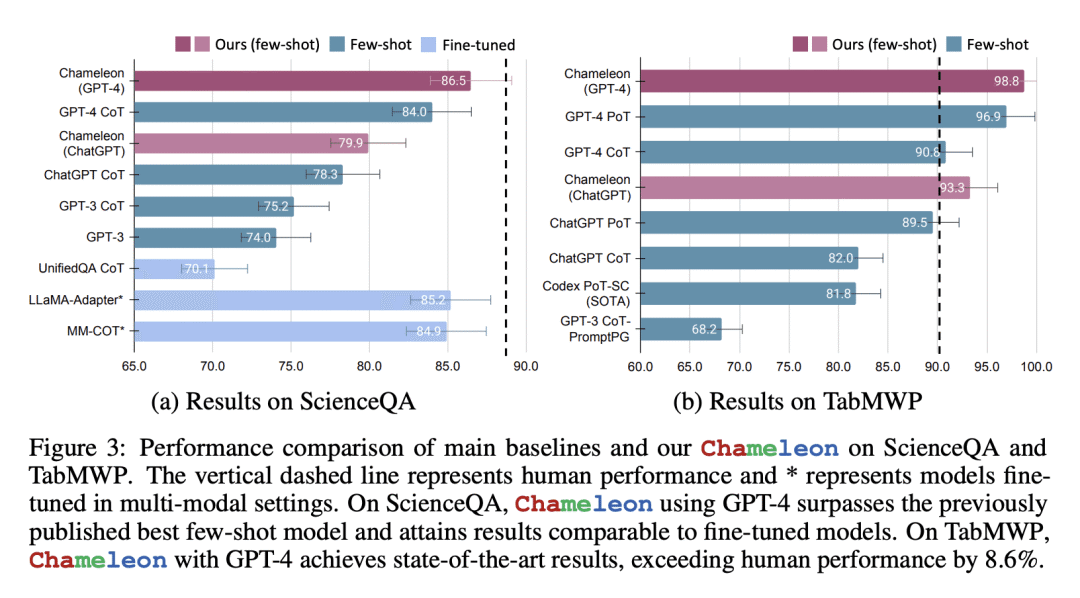
Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in various natural language processing tasks with emergent abilities. However, they face inherent limitations, such as an inability to access up-to-date information, utilize external tools, or perform precise mathematical reasoning. In this paper, we introduce Chameleon, a plug-and-play compositional reasoning framework that augments LLMs to help address these challenges. Chameleon synthesizes programs to compose various tools, including LLM models, off-the-shelf vision models, web search engines, Python functions, and rule-based modules tailored to user interests. Built on top of an LLM as a natural language planner, Chameleon infers the appropriate sequence of tools to compose and execute in order to generate a final response. We showcase the adaptability and effectiveness of Chameleon on two tasks: ScienceQA and TabMWP. Notably, Chameleon with GPT-4 achieves an 86.54% accuracy on ScienceQA, significantly improving upon the best published few-shot model by 11.37%; using GPT-4 as the underlying LLM, Chameleon achieves a 17.8% increase over the state-of-the-art model, leading to a 98.78% overall accuracy on TabMWP. Further studies suggest that using GPT-4 as a planner exhibits more consistent and rational tool selection and is able to infer potential constraints given the instructions, compared to other LLMs like ChatGPT.
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢