✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,matlab项目合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击👇
❤️ 内容介绍
鲁棒极限学习机(Robust Extreme Learning Machine, RELM)是一种基于极限学习机(Extreme Learning Machine, ELM)的算法,用于实现数据分类任务。RELM通过引入鲁棒损失函数,提高了ELM在面对噪声和异常值时的鲁棒性能。
RELM的实现步骤如下:
数据预处理:对原始数据进行预处理,包括数据清洗、特征选择和特征缩放等操作。
构建输入矩阵:将预处理后的数据按照矩阵的形式表示,其中每一行代表一个样本的特征,每一列代表一个特征。
随机初始化输入权重:随机生成输入层到隐藏层的权重矩阵,其中隐藏层的节点数可以根据经验或者交叉验证进行选择。
计算隐藏层输出:使用ReLU(Rectified Linear Unit)激活函数计算隐藏层的输出,即将输入矩阵与输入权重矩阵相乘,并将结果进行非线性变换。
求解输出权重:使用最小二乘法或者正则化方法求解输出权重矩阵,将隐藏层输出与样本的标签进行拟合。
预测分类结果:使用求解得到的输出权重矩阵,将测试样本的特征与隐藏层输出进行相乘,并通过激活函数得到预测的分类结果。
模型评估:使用评估指标(如准确率、精确率、召回率等)对模型进行评估,可以使用交叉验证等方法进行评估结果的稳定性。
通过以上步骤,可以使用RELM实现数据的分类任务。相比于传统的ELM算法,RELM在面对噪声和异常值时具有更好的鲁棒性能,可以提高分类模型的准确性和稳定性。
🔥核心代码
function [TrainingTime, TestingTime, TrainingAccuracy, TestingAccuracy] = elm(TrainingData_File, TestingData_File, Elm_Type, NumberofHiddenNeurons, ActivationFunction)% Usage: elm(TrainingData_File, TestingData_File, Elm_Type, NumberofHiddenNeurons, ActivationFunction)% OR: [TrainingTime, TestingTime, TrainingAccuracy, TestingAccuracy] = elm(TrainingData_File, TestingData_File, Elm_Type, NumberofHiddenNeurons, ActivationFunction)%% Input:% TrainingData_File - Filename of training data set% TestingData_File - Filename of testing data set% Elm_Type - 0 for regression; 1 for (both binary and multi-classes) classification% NumberofHiddenNeurons - Number of hidden neurons assigned to the ELM% ActivationFunction - Type of activation function:% 'sig' for Sigmoidal function% 'sin' for Sine function% 'hardlim' for Hardlim function% 'tribas' for Triangular basis function% 'radbas' for Radial basis function (for additive type of SLFNs instead of RBF type of SLFNs)%% Output:% TrainingTime - Time (seconds) spent on training ELM% TestingTime - Time (seconds) spent on predicting ALL testing data% TrainingAccuracy - Training accuracy:% RMSE for regression or correct classification rate for classification% TestingAccuracy - Testing accuracy:% RMSE for regression or correct classification rate for classification%% MULTI-CLASSE CLASSIFICATION: NUMBER OF OUTPUT NEURONS WILL BE AUTOMATICALLY SET EQUAL TO NUMBER OF CLASSES% FOR EXAMPLE, if there are 7 classes in all, there will have 7 output% neurons; neuron 5 has the highest output means input belongs to 5-th class%% Sample1 regression: [TrainingTime, TestingTime, TrainingAccuracy, TestingAccuracy] = elm('sinc_train', 'sinc_test', 0, 20, 'sig')% Sample2 classification: elm('diabetes_train', 'diabetes_test', 1, 20, 'sig')%%%%% Authors: MR QIN-YU ZHU AND DR GUANG-BIN HUANG%%%% NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, SINGAPORE%%%% EMAIL: EGBHUANG@NTU.EDU.SG; GBHUANG@IEEE.ORG%%%% WEBSITE: http://www.ntu.edu.sg/eee/icis/cv/egbhuang.htm%%%% DATE: APRIL 2004%%%%%%%%%%% Macro definitionREGRESSION=0;CLASSIFIER=1;%%%%%%%%%%% Load training datasettrain_data=load(TrainingData_File);T=train_data(:,1)';P=train_data(:,2:size(train_data,2))';clear train_data; % Release raw training data array%%%%%%%%%%% Load testing datasettest_data=load(TestingData_File);TV.T=test_data(:,1)';TV.P=test_data(:,2:size(test_data,2))';clear test_data; % Release raw testing data arrayNumberofTrainingData=size(P,2);NumberofTestingData=size(TV.P,2);NumberofInputNeurons=size(P,1);if Elm_Type~=REGRESSION%%%%%%%%%%%% Preprocessing the data of classificationsorted_target=sort(cat(2,T,TV.T),2);label=zeros(1,1); % Find and save in 'label' class label from training and testing data setslabel(1,1)=sorted_target(1,1);j=1;for i = 2:(NumberofTrainingData+NumberofTestingData)if sorted_target(1,i) ~= label(1,j)j=j+1;label(1,j) = sorted_target(1,i);endendnumber_class=j;NumberofOutputNeurons=number_class;%%%%%%%%%% Processing the targets of trainingtemp_T=zeros(NumberofOutputNeurons, NumberofTrainingData);for i = 1:NumberofTrainingDatafor j = 1:number_classif label(1,j) == T(1,i)break;endendtemp_T(j,i)=1;endT=temp_T*2-1;%%%%%%%%%% Processing the targets of testingtemp_TV_T=zeros(NumberofOutputNeurons, NumberofTestingData);for i = 1:NumberofTestingDatafor j = 1:number_classif label(1,j) == TV.T(1,i)break;endendtemp_TV_T(j,i)=1;endTV.T=temp_TV_T*2-1;end % end if of Elm_Type%%%%%%%%%%% Calculate weights & biasesstart_time_train=cputime;%%%%%%%%%%% Random generate input weights InputWeight (w_i) and biases BiasofHiddenNeurons (b_i) of hidden neuronsInputWeight=rand(NumberofHiddenNeurons,NumberofInputNeurons)*2-1;BiasofHiddenNeurons=rand(NumberofHiddenNeurons,1);tempH=InputWeight*P;clear P; % Release input of training dataind=ones(1,NumberofTrainingData);BiasMatrix=BiasofHiddenNeurons(:,ind); % Extend the bias matrix BiasofHiddenNeurons to match the demention of HtempH=tempH+BiasMatrix;%%%%%%%%%%% Calculate hidden neuron output matrix Hswitch lower(ActivationFunction)case {'sig','sigmoid'}%%%%%%%% SigmoidH = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-tempH));case {'sin','sine'}%%%%%%%% SineH = sin(tempH);case {'hardlim'}%%%%%%%% Hard LimitH = double(hardlim(tempH));case {'tribas'}%%%%%%%% Triangular basis functionH = tribas(tempH);case {'radbas'}%%%%%%%% Radial basis functionH = radbas(tempH);%%%%%%%% More activation functions can be added hereendclear tempH; % Release the temparary array for calculation of hidden neuron output matrix H%%%%%%%%%%% Calculate output weights OutputWeight (beta_i)OutputWeight=pinv(H') * T'; % implementation without regularization factor //refer to 2006 Neurocomputing paper%OutputWeight=inv(eye(size(H,1))/C+H * H') * H * T'; % faster method 1 //refer to 2012 IEEE TSMC-B paper%implementation; one can set regularizaiton factor C properly in classification applications%OutputWeight=(eye(size(H,1))/C+H * H') \ H * T'; % faster method 2 //refer to 2012 IEEE TSMC-B paper%implementation; one can set regularizaiton factor C properly in classification applications%If you use faster methods or kernel method, PLEASE CITE in your paper properly:%Guang-Bin Huang, Hongming Zhou, Xiaojian Ding, and Rui Zhang, "Extreme Learning Machine for Regression and Multi-Class Classification," submitted to IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, October 2010.end_time_train=cputime;TrainingTime=end_time_train-start_time_train % Calculate CPU time (seconds) spent for training ELM%%%%%%%%%%% Calculate the training accuracyY=(H' * OutputWeight)'; % Y: the actual output of the training dataif Elm_Type == REGRESSIONTrainingAccuracy=sqrt(mse(T - Y)) % Calculate training accuracy (RMSE) for regression caseendclear H;%%%%%%%%%%% Calculate the output of testing inputstart_time_test=cputime;tempH_test=InputWeight*TV.P;clear TV.P; % Release input of testing dataind=ones(1,NumberofTestingData);BiasMatrix=BiasofHiddenNeurons(:,ind); % Extend the bias matrix BiasofHiddenNeurons to match the demention of HtempH_test=tempH_test + BiasMatrix;switch lower(ActivationFunction)case {'sig','sigmoid'}%%%%%%%% SigmoidH_test = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-tempH_test));case {'sin','sine'}%%%%%%%% SineH_test = sin(tempH_test);case {'hardlim'}%%%%%%%% Hard LimitH_test = hardlim(tempH_test);case {'tribas'}%%%%%%%% Triangular basis functionH_test = tribas(tempH_test);case {'radbas'}%%%%%%%% Radial basis functionH_test = radbas(tempH_test);%%%%%%%% More activation functions can be added hereendTY=(H_test' * OutputWeight)'; % TY: the actual output of the testing dataend_time_test=cputime;TestingTime=end_time_test-start_time_test % Calculate CPU time (seconds) spent by ELM predicting the whole testing dataif Elm_Type == REGRESSIONTestingAccuracy=sqrt(mse(TV.T - TY)) % Calculate testing accuracy (RMSE) for regression caseendif Elm_Type == CLASSIFIER%%%%%%%%%% Calculate training & testing classification accuracyMissClassificationRate_Training=0;MissClassificationRate_Testing=0;for i = 1 : size(T, 2)[x, label_index_expected]=max(T(:,i));[x, label_index_actual]=max(Y(:,i));if label_index_actual~=label_index_expectedMissClassificationRate_Training=MissClassificationRate_Training+1;endendTrainingAccuracy=1-MissClassificationRate_Training/size(T,2)for i = 1 : size(TV.T, 2)[x, label_index_expected]=max(TV.T(:,i));[x, label_index_actual]=max(TY(:,i));if label_index_actual~=label_index_expectedMissClassificationRate_Testing=MissClassificationRate_Testing+1;endendTestingAccuracy=1-MissClassificationRate_Testing/size(TV.T,2)end
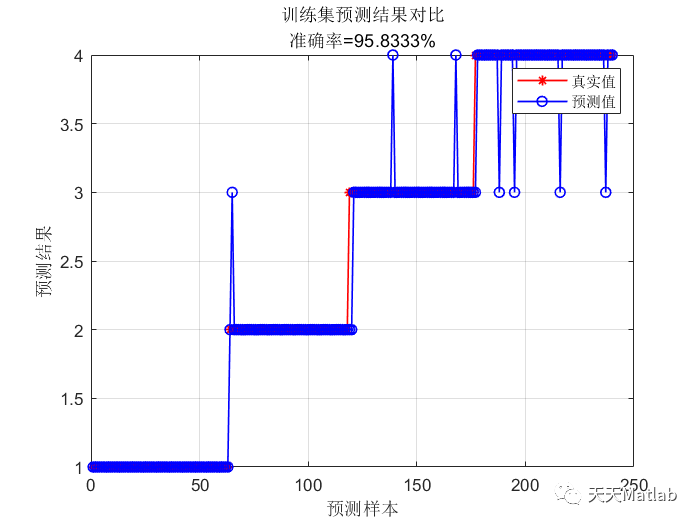
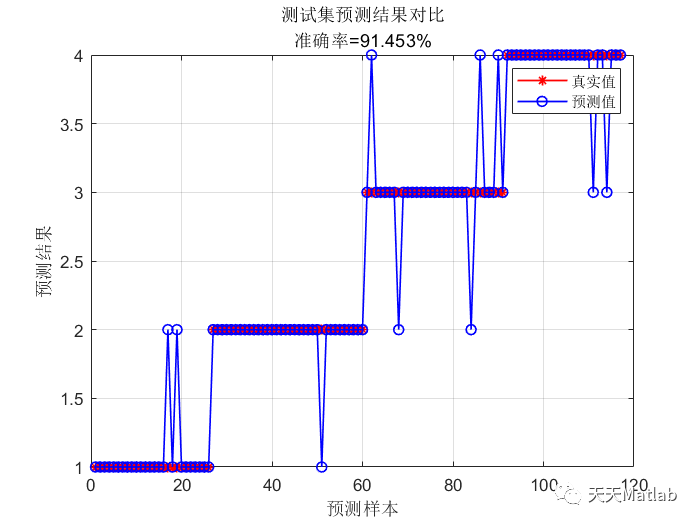
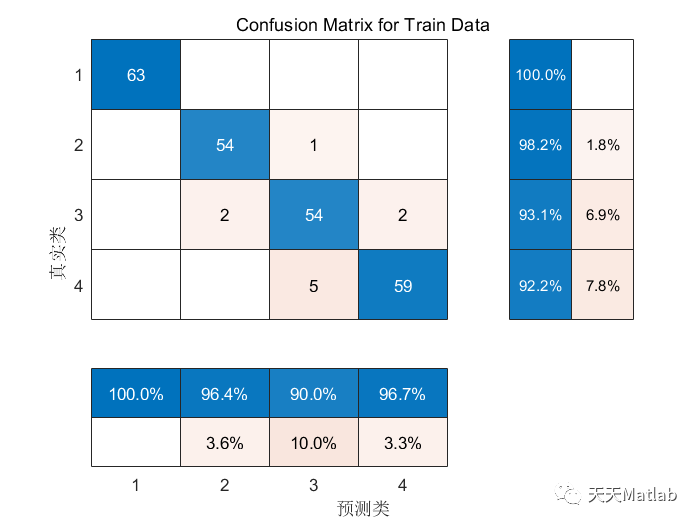
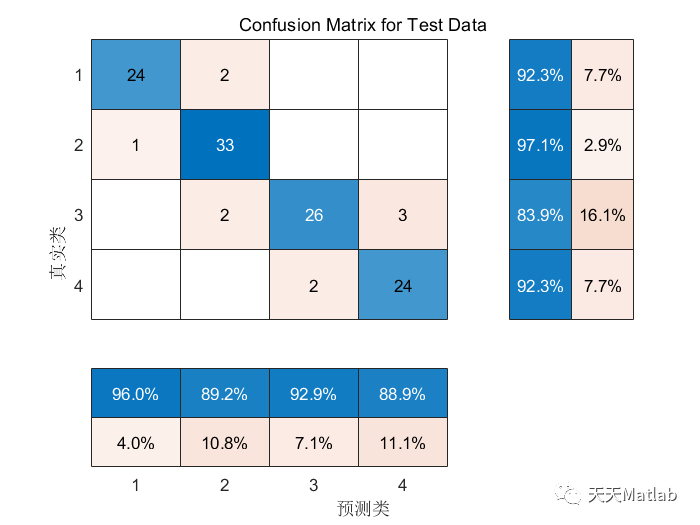
❤️ 运行结果
⛄ 参考文献
[1] 焦广利,张璐,钟麦英.基于鲁棒极限学习机的污泥膨胀智能检测方法[J].山东科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2022(003):041.
[2] 王亚.基于极限学习机改进模型的煤矿突水水源识别研究[D].安徽理工大学[2023-09-02].DOI:CNKI:CDMD:1.1018.195306.
[3] 王石磊,陆慧娟,关伟,等.一种粒子群RELM的基因表达数据分类方法[J].中国计量学院学报, 2015, 26(2):6.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-1540.2015.02.018.
⛳️ 代码获取关注我
❤️部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
❤️ 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料
🍅 仿真咨询
1 各类智能优化算法改进及应用
生产调度、经济调度、装配线调度、充电优化、车间调度、发车优化、水库调度、三维装箱、物流选址、货位优化、公交排班优化、充电桩布局优化、车间布局优化、集装箱船配载优化、水泵组合优化、解医疗资源分配优化、设施布局优化、可视域基站和无人机选址优化
2 机器学习和深度学习方面
卷积神经网络(CNN)、LSTM、支持向量机(SVM)、最小二乘支持向量机(LSSVM)、极限学习机(ELM)、核极限学习机(KELM)、BP、RBF、宽度学习、DBN、RF、RBF、DELM、XGBOOST、TCN实现风电预测、光伏预测、电池寿命预测、辐射源识别、交通流预测、负荷预测、股价预测、PM2.5浓度预测、电池健康状态预测、水体光学参数反演、NLOS信号识别、地铁停车精准预测、变压器故障诊断
2.图像处理方面
图像识别、图像分割、图像检测、图像隐藏、图像配准、图像拼接、图像融合、图像增强、图像压缩感知
3 路径规划方面
旅行商问题(TSP)、车辆路径问题(VRP、MVRP、CVRP、VRPTW等)、无人机三维路径规划、无人机协同、无人机编队、机器人路径规划、栅格地图路径规划、多式联运运输问题、车辆协同无人机路径规划、天线线性阵列分布优化、车间布局优化
4 无人机应用方面
无人机路径规划、无人机控制、无人机编队、无人机协同、无人机任务分配
、无人机安全通信轨迹在线优化
5 无线传感器定位及布局方面
传感器部署优化、通信协议优化、路由优化、目标定位优化、Dv-Hop定位优化、Leach协议优化、WSN覆盖优化、组播优化、RSSI定位优化
6 信号处理方面
信号识别、信号加密、信号去噪、信号增强、雷达信号处理、信号水印嵌入提取、肌电信号、脑电信号、信号配时优化
7 电力系统方面
微电网优化、无功优化、配电网重构、储能配置
8 元胞自动机方面
交通流 人群疏散 病毒扩散 晶体生长 火灾扩散
9 雷达方面
卡尔曼滤波跟踪、航迹关联、航迹融合、状态估计
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除




评论
沙发等你来抢