
以下文章来源于微信公众号:算法美食屋
作者:明训
链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/qHUxO6Ml-O1PCK1bc9uD7g
本文仅用于学术分享,如有侵权,请联系后台作删文处理

公众号江大白后台回复关键词:langchain,获取本文notebook源代码。
9个范例功能列表如下:
# 在我们开始前,安装需要的依赖
!pip install langchain
!pip install openai
!pip install tiktoken
!pip install faiss-cpu
openai_api_key='YOUR_API_KEY'
# 使用你自己的OpenAI API key
一, 文本总结(Summarization)
1,短文本总结
# Summaries Of Short Text
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain import PromptTemplate
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, model_name = 'gpt-3.5-turbo', openai_api_key=openai_api_key) # 初始化LLM模型
# 创建模板
template = """
%INSTRUCTIONS:
Please summarize the following piece of text.
Respond in a manner that a 5 year old would understand.
%TEXT:
{text}
"""
# 创建一个 Lang Chain Prompt 模板,稍后可以插入值
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["text"],
template=template,
)
confusing_text = """
For the next 130 years, debate raged.
Some scientists called Prototaxites a lichen, others a fungus, and still others clung to the notion that it was some kind of tree.
“The problem is that when you look up close at the anatomy, it’s evocative of a lot of different things, but it’s diagnostic of nothing,” says Boyce, an associate professor in geophysical sciences and the Committee on Evolutionary Biology.
“And it’s so damn big that when whenever someone says it’s something, everyone else’s hackles get up: ‘How could you have a lichen 20 feet tall?’”
"""
print ("------- Prompt Begin -------")
# 打印模板内容
final_prompt = prompt.format(text=confusing_text)
print(final_prompt)
print ("------- Prompt End -------")
------- Prompt Begin -------
%INSTRUCTIONS:
Please summarize the following piece of text.
Respond in a manner that a 5 year old would understand.
%TEXT:
For the next 130 years, debate raged.
Some scientists called Prototaxites a lichen, others a fungus, and still others clung to the notion that it was some kind of tree.
“The problem is that when you look up close at the anatomy, it’s evocative of a lot of different things, but it’s diagnostic of nothing,” says Boyce, an associate professor in geophysical sciences and the Committee on Evolutionary Biology.
“And it’s so damn big that when whenever someone says it’s something, everyone else’s hackles get up: ‘How could you have a lichen 20 feet tall?’”
------- Prompt End -------
output = llm(final_prompt)
print (output)
People argued for a long time about what Prototaxites was. Some thought it was a lichen, some thought it was a fungus, and some thought it was a tree. But it was hard to tell for sure because it looked like different things up close and it was really, really big.
2,长文本总结
# Summaries Of Longer Text
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain.chains.summarize import load_summarize_chain
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
with open('wonderland.txt', 'r') as file:
text = file.read() # 文章本身是爱丽丝梦游仙境
# 打印小说的前285个字符
print (text[:285])
The Project Gutenberg eBook of Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland, by Lewis Carroll
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and
most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions
whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it unde
num_tokens = llm.get_num_tokens(text)
print (f"There are {num_tokens} tokens in your file")
# 全文一共4w8词
# 很明显这样的文本量是无法直接送进LLM进行处理和生成的
There are 48613 tokens in your file
解决长文本的方式无非是'chunking','splitting' 原文本为小的段落/分割部分
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(separators=["\n\n", "\n"], chunk_size=5000, chunk_overlap=350)
# 虽然我使用的是 RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter,但是你也可以使用其他工具
docs = text_splitter.create_documents([text])
print (f"You now have {len(docs)} docs intead of 1 piece of text")
You now have 36 docs intead of 1 piece of text
现在就需要一个 Lang Chain 工具,将分段文本送入LLM进行summary
# 设置 lang chain
# 使用 map_reduce的chain_type,这样可以将多个文档合并成一个
chain = load_summarize_chain(llm=llm, chain_type='map_reduce') # verbose=True 展示运行日志
# Use it. This will run through the 36 documents, summarize the chunks, then get a summary of the summary.
# 典型的map reduce的思路去解决问题,将文章拆分成多个部分,再将多个部分分别进行 summarize,最后再进行 合并,对 summarys 进行 summary
output = chain.run(docs)
print (output)
# Try yourself
Alice follows a white rabbit down a rabbit hole and finds herself in a strange world full of peculiar characters. She experiences many strange adventures and is asked to settle disputes between the characters. In the end, she is in a court of justice with the King and Queen of Hearts and is questioned by the King. Alice reads a set of verses and has a dream in which she remembers a secret. Project Gutenberg is a library of electronic works founded by Professor Michael S. Hart and run by volunteers.
二,文档问答(QA based Documents)
需要向LLM传递能够让他参考的上下文信息 需要向LLM准确地传达我们的问题
1,短文本问答
# 概括来说,使用文档作为上下文进行QA系统的构建过程类似于 llm(your context + your question) = your answer
# Simple Q&A Example
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
context = """
Rachel is 30 years old
Bob is 45 years old
Kevin is 65 years old
"""
question = "Who is under 40 years old?"
output = llm(context + question)
print (output.strip())
Rachel is under 40 years old.
2,长文本问答
from langchain import OpenAI
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain.document_loaders import TextLoader
from langchain.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
loader = TextLoader('wonderland.txt') # 载入一个长文本,我们还是使用爱丽丝漫游仙境这篇小说作为输入
doc = loader.load()
print (f"You have {len(doc)} document")
print (f"You have {len(doc[0].page_content)} characters in that document")
You have 1 document
You have 164014 characters in that document
# 将小说分割成多个部分
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=3000, chunk_overlap=400)
docs = text_splitter.split_documents(doc)
# 获取字符的总数,以便可以计算平均值
num_total_characters = sum([len(x.page_content) for x in docs])
print (f"Now you have {len(docs)} documents that have an average of {num_total_characters / len(docs):,.0f} characters (smaller pieces)")
Now you have 62 documents that have an average of 2,846 characters (smaller pieces)
# 设置 embedding 引擎
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
# Embed 文档,然后使用伪数据库将文档和原始文本结合起来
# 这一步会向 OpenAI 发起 API 请求
docsearch = FAISS.from_documents(docs, embeddings)
# 创建QA-retrieval chain
qa = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=llm, chain_type="stuff", retriever=docsearch.as_retriever())
query = "What does the author describe the Alice following with?"
qa.run(query)
# 这个过程中,检索器会去获取类似的文件部分,并结合你的问题让 LLM 进行推理,最后得到答案
# 这一步还有很多可以细究的步骤,比如如何选择最佳的分割大小,如何选择最佳的 embedding 引擎,如何选择最佳的检索器等等
# 同时也可以选择云端向量存储
' The author describes Alice following a White Rabbit with pink eyes.'
三,信息抽取(Extraction)
从句子中提取结构化行以插入数据库 从长文档中提取多行以插入数据库 从用户查询中提取参数以进行 API 调用 最近最火的 Extraction 库是 KOR
1,手动格式转换
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate, HumanMessagePromptTemplate
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
chat_model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model='gpt-3.5-turbo', openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
# Vanilla Extraction
instructions = """
You will be given a sentence with fruit names, extract those fruit names and assign an emoji to them
Return the fruit name and emojis in a python dictionary
"""
fruit_names = """
Apple, Pear, this is an kiwi
"""
# Make your prompt which combines the instructions w/ the fruit names
prompt = (instructions + fruit_names)
# Call the LLM
output = chat_model([HumanMessage(content=prompt)])
print (output.content)
print (type(output.content))
{'Apple': '🍎', 'Pear': '🍐', 'kiwi': '🥝'}
<class 'str'>
output_dict = eval(output.content) #利用python中的eval函数手动转换格式
print (output_dict)
print (type(output_dict))
2,自动格式转换
# 解析输出并获取结构化的数据
from langchain.output_parsers import StructuredOutputParser, ResponseSchema
response_schemas = [
ResponseSchema(name="artist", description="The name of the musical artist"),
ResponseSchema(name="song", description="The name of the song that the artist plays")
]
# 解析器将会把LLM的输出使用我定义的schema进行解析并返回期待的结构数据给我
output_parser = StructuredOutputParser.from_response_schemas(response_schemas)
format_instructions = output_parser.get_format_instructions()
print(format_instructions)
The output should be a markdown code snippet formatted in the following schema, including the leading and trailing "\`\`\`json" and "\`\`\`":
```json
{
"artist": string // The name of the musical artist
"song": string // The name of the song that the artist plays
}
```
# 这个 Prompt 与之前我们构建 Chat Model 时 Prompt 不同
# 这个 Prompt 是一个 ChatPromptTemplate,它会自动将我们的输出转化为 python 对象
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate(
messages=[
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("Given a command from the user, extract the artist and song names \n \
{format_instructions}\n{user_prompt}")
],
input_variables=["user_prompt"],
partial_variables={"format_instructions": format_instructions}
)
artist_query = prompt.format_prompt(user_prompt="I really like So Young by Portugal. The Man")
print(artist_query.messages[0].content)
Given a command from the user, extract the artist and song names
The output should be a markdown code snippet formatted in the following schema, including the leading and trailing "\`\`\`json" and "\`\`\`":
```json
{
"artist": string // The name of the musical artist
"song": string // The name of the song that the artist plays
}
```
I really like So Young by Portugal. The Man
artist_output = chat_model(artist_query.to_messages())
output = output_parser.parse(artist_output.content)
print (output)
print (type(output))
# 这里要注意的是,因为我们使用的 turbo 模型,生成的结果并不一定是每次都一致的
# 替换成gpt4模型可能是更好的选择
{'artist': 'Portugal. The Man', 'song': 'So Young'}
<class 'dict'>
四,结果评估(Evaluation)
# Embeddings, store, and retrieval
from langchain.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
# Model and doc loader
from langchain import OpenAI
from langchain.document_loaders import TextLoader
# Eval
from langchain.evaluation.qa import QAEvalChain
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
# 还是使用爱丽丝漫游仙境作为文本输入
loader = TextLoader('wonderland.txt')
doc = loader.load()
print (f"You have {len(doc)} document")
print (f"You have {len(doc[0].page_content)} characters in that document")
You have 1 document
You have 164014 characters in that document
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=3000, chunk_overlap=400)
docs = text_splitter.split_documents(doc)
# Get the total number of characters so we can see the average later
num_total_characters = sum([len(x.page_content) for x in docs])
print (f"Now you have {len(docs)} documents that have an average of {num_total_characters / len(docs):,.0f} characters (smaller pieces)")
Now you have 62 documents that have an average of 2,846 characters (smaller pieces)
# Embeddings and docstore
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
docsearch = FAISS.from_documents(docs, embeddings)
chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=llm, chain_type="stuff", retriever=docsearch.as_retriever(), input_key="question")
# 注意这里的 input_key 参数,这个参数告诉了 chain 我的问题在字典中的哪个 key 里
# 这样 chain 就会自动去找到问题并将其传递给 LLM
question_answers = [
{'question' : "Which animal give alice a instruction?", 'answer' : 'rabbit'},
{'question' : "What is the author of the book", 'answer' : 'Elon Mask'}
]
predictions = chain.apply(question_answers)
predictions
# 使用LLM模型进行预测,并将答案与我提供的答案进行比较,这里信任我自己提供的人工答案是正确的
[{'question': 'Which animal give alice a instruction?',
'answer': 'rabbit',
'result': ' The Caterpillar gave Alice instructions.'},
{'question': 'What is the author of the book',
'answer': 'Elon Mask',
'result': ' The author of the book is Lewis Carroll.'}]
# Start your eval chain
eval_chain = QAEvalChain.from_llm(llm)
graded_outputs = eval_chain.evaluate(question_answers,
predictions,
question_key="question",
prediction_key="result",
answer_key='answer')
graded_outputs
[{'text': ' INCORRECT'}, {'text': ' INCORRECT'}]
五,数据库问答(Querying Tabular Data)
# 使用自然语言查询一个 SQLite 数据库,我们将使用旧金山树木数据集
# Don't run following code if you don't run sqlite and follow db
from langchain import OpenAI, SQLDatabase, SQLDatabaseChain
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
sqlite_db_path = 'data/San_Francisco_Trees.db'
db = SQLDatabase.from_uri(f"sqlite:///{sqlite_db_path}")
db_chain = SQLDatabaseChain(llm=llm, database=db, verbose=True)
db_chain.run("How many Species of trees are there in San Francisco?")
Find which table to use Find which column to use Construct the correct sql query Execute that query Get the result Return a natural language reponse back
confirm LLM result via pandas
import sqlite3
import pandas as pd
# Connect to the SQLite database
connection = sqlite3.connect(sqlite_db_path)
# Define your SQL query
query = "SELECT count(distinct qSpecies) FROM SFTrees"
# Read the SQL query into a Pandas DataFrame
df = pd.read_sql_query(query, connection)
# Close the connection
connection.close()
# Display the result in the first column first cell
print(df.iloc[0,0])
六,代码理解(Code Understanding)
# Helper to read local files
import os
# Vector Support
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
# Model and chain
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
# Text splitters
from langchain.text_splitter import CharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.document_loaders import TextLoader
llm = ChatOpenAI(model='gpt-3.5-turbo', openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(disallowed_special=(), openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
root_dir = '/content/drive/MyDrive/thefuzz-master'
docs = []
# Go through each folder
for dirpath, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(root_dir):
# Go through each file
for file in filenames:
try:
# Load up the file as a doc and split
loader = TextLoader(os.path.join(dirpath, file), encoding='utf-8')
docs.extend(loader.load_and_split())
except Exception as e:
pass
print (f"You have {len(docs)} documents\n")
print ("------ Start Document ------")
print (docs[0].page_content[:300])
You have 175 documents
------ Start Document ------
from timeit import timeit
import math
import csv
iterations = 100000
reader = csv.DictReader(open('data/titledata.csv'), delimiter='|')
titles = [i['custom_title'] for i in reader]
title_blob = '\n'.join(titles)
cirque_strings = [
"cirque du soleil - zarkana - las vegas",
"cirque du sol
docsearch = FAISS.from_documents(docs, embeddings)
# Get our retriever ready
qa = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=llm, chain_type="stuff", retriever=docsearch.as_retriever())
query = "What function do I use if I want to find the most similar item in a list of items?"
output = qa.run(query)
print (output)
You can use the `process.extractOne()` function from `thefuzz` package to find the most similar item in a list of items. For example:
```
from thefuzz import process
choices = ["New York Yankees", "Boston Red Sox", "Chicago Cubs", "Los Angeles Dodgers"]
query = "new york mets vs atlanta braves"
best_match = process.extractOne(query, choices)
print(best_match)
```
This will output:
```
('New York Yankees', 50)
```
Where `('New York Yankees', 50)` means that the closest match found was "New York Yankees" with a score of 50 (out of 100).
query = "Can you write the code to use the process.extractOne() function? Only respond with code. No other text or explanation"
output = qa.run(query)
print(output)
process.extractOne(query, choices)
七,API交互(Interacting with APIs)
from langchain.chains import APIChain
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
api_docs = """
BASE URL: https://restcountries.com/
API Documentation:
The API endpoint /v3.1/name/{name} Used to find informatin about a country. All URL parameters are listed below:
- name: Name of country - Ex: italy, france
The API endpoint /v3.1/currency/{currency} Uesd to find information about a region. All URL parameters are listed below:
- currency: 3 letter currency. Example: USD, COP
Woo! This is my documentation
"""
chain_new = APIChain.from_llm_and_api_docs(llm, api_docs, verbose=True)
chain_new.run('Can you tell me information about france?')

' France is an officially-assigned, independent country located in Western Europe. Its capital is Paris and its official language is French. Its currency is the Euro (€). It has a population of 67,391,582 and its borders are with Andorra, Belgium, Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, Monaco, Spain, and Switzerland.'
chain_new.run('Can you tell me about the currency COP?')

' The currency of Colombia is the Colombian peso (COP), symbolized by the "$" sign.'
八,聊天机器人(Chatbots)
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain import LLMChain
from langchain.prompts.prompt import PromptTemplate
# Chat specific components
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
template = """
You are a chatbot that is unhelpful.
Your goal is to not help the user but only make jokes.
Take what the user is saying and make a joke out of it
{chat_history}
Human: {human_input}
Chatbot:"""
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["chat_history", "human_input"],
template=template
)
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history")
llm_chain = LLMChain(
llm=OpenAI(openai_api_key=openai_api_key),
prompt=prompt,
verbose=True,
memory=memory
)
llm_chain.predict(human_input="Is an pear a fruit or vegetable?")

' An pear is a fruit, but a vegetable-pear is a pun-ishable offense!'
llm_chain.predict(human_input="What was one of the fruits I first asked you about?")
# 这里第二个问题的答案是来自于第一个答案本身的,因此我们使用到了 memory

" An pear - but don't let it get to your core!"
九,智能体(Agents)
# Helpers
import os
import json
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
# Agent imports
from langchain.agents import load_tools
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent
# Tool imports
from langchain.agents import Tool
from langchain.utilities import GoogleSearchAPIWrapper
from langchain.utilities import TextRequestsWrapper
os.environ["GOOGLE_CSE_ID"] = "YOUR_GOOGLE_CSE_ID"
os.environ["GOOGLE_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_GOOGLE_API_KEY"
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
search = GoogleSearchAPIWrapper()
requests = TextRequestsWrapper()
toolkit = [
Tool(
name = "Search",
func=search.run,
description="useful for when you need to search google to answer questions about current events"
),
Tool(
name = "Requests",
func=requests.get,
description="Useful for when you to make a request to a URL"
),
]
agent = initialize_agent(toolkit, llm, agent="zero-shot-react-description", verbose=True, return_intermediate_steps=True)
response = agent({"input":"What is the capital of canada?"})
response['output']

'Ottawa is the capital of Canada.'
response = agent({"input":"Tell me what the comments are about on this webpage https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=34425779"})
response['output']
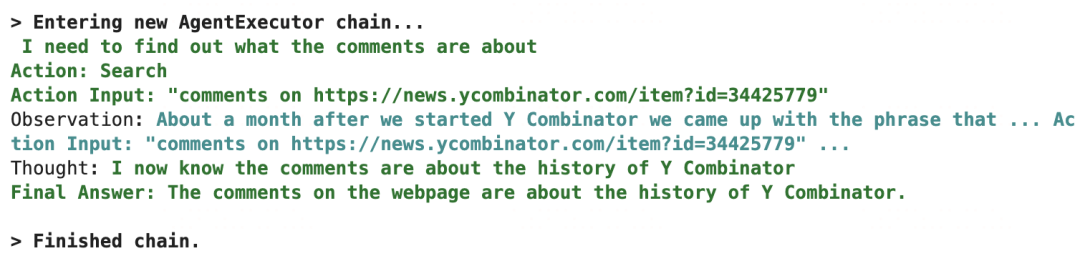
'The comments on the webpage are about the history of Y Combinator.'
推荐阅读

AIHIA | AI人才创新发展联盟2023年盟友招募

AIHIA | AI人才创新发展联盟2023年盟友招募

AI融资 | 智能物联网公司阿加犀获得高通5000W融资

AI融资 | 智能物联网公司阿加犀获得高通5000W融资

Yolov5应用 | 家庭安防告警系统全流程及代码讲解

江大白 | 这些年从0转行AI行业的一些感悟

Yolov5应用 | 家庭安防告警系统全流程及代码讲解

江大白 | 这些年从0转行AI行业的一些感悟

《AI未来星球》陪伴你在AI行业成长的社群,各项福利重磅开放:
(1)198元《31节课入门人工智能》视频课程;
(2)大白花费近万元购买的各类数据集;
(3)每月自习活动,每月17日星球会员日,各类奖品送不停;
(4)加入《AI未来星球》内部微信群;
还有各类直播时分享的文件、研究报告,一起扫码加入吧!


大家一起加油! 
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢