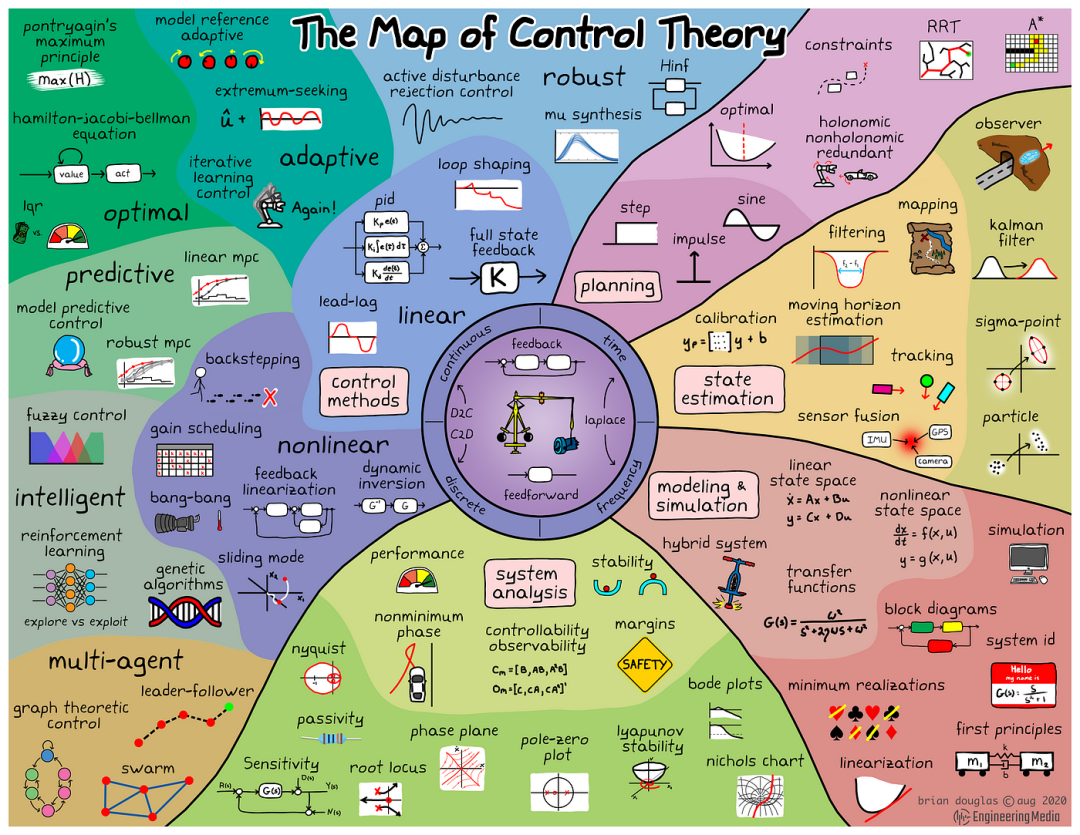
Brian Douglas绘制
系列课程引入
系列课程引入

课程框架介绍
课程框架介绍
序号 | 时间 | 主讲人 | 主题 |
1 | 1月12日(已分享) | 郭雷 | 系统控制之美 |
2 | 4月2日 | 黄一 | 走马观花看控制发展简史 |
3 | 4月9日 | 赵成 | PID控制的基础理论 |
4 | 4月23日 | 黄一 | 自抗扰控制:思想、应用及理论分析 |
5 | 4月30日 | 李婵颖 | 自适应控制理论 |
6 | 5月7日 | 赵文虓 | 系统辨识 |
7 | 5月14日 | 赵延龙 | 集值系统的辨识与控制 |
8 | 5月21日 | 刘志新 | 多主体系统的分析与控制 |
9 | 5月28日 | 郭宝珠 | 分布参数系统控制 |
10 | 6月4日 | 齐洪胜 | 逻辑动态系统的分析与控制 |
讲师团介绍
讲师团介绍



李婵颖,现任中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院研究员,本科毕业于四川大学数学系,获中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院硕士及博士学位。研究兴趣包括自适应控制、采样系统以及航天控制等。主持国家自然科学基金委杰出青年科学基金以及优秀青年科学基金,获第十九届中国青年女科学家奖、第四届中国工业与应用数学学会青年科技奖以及第33届中国控制会议最佳论文奖等。目前担任Automatica、Mathematical Control and Related Fields以及Journal of Systems Science and Complexity等杂志编委。






课程简介与推荐资料
课程简介与推荐资料
Special Issue on the evolving history of control,IEEE Control Systems, 1996, 16(3) Stuart Bennett. A brief history of automatic control.IEEE Control Systems, 1996, 16(3): 17-25. 黄一,走马观花看控制发展简史,《系统与控制纵横》2021年第1期 Gene F. Franklin, J. David Powell and Abbas Emami-Naeini, 动态系统的反馈控制,电子工业出版社, 2004. Richard C. Dorf and Robert H. Bishop, 现代控制系统,高等教育出版社,2001.
在自适应控制领域,利用 “必然等价” 原则设计出一个自适应控制算法一般并不困难,真正的困难在于对所设计出的控制算法,能否从理论上保证被控闭环系统具有稳定性与收敛性等所需要的良好性能。不幸的是,由于自适应控制系统的结构在本质上,是由一组很复杂的非线性与非平稳随机动态方程组所刻画 (即使被控对象是线性系统亦然),这就使得为其建立稳定性与收敛性的数学理论带来超出预料的研究困难。
实际上,任何一个功能较为高级的 “智能化” 系统,往往都具有一定程度的 “复杂性” 的反馈结构,这似乎是 “智能化” 的必然 “代价”。但从理论研究上来讲,最容易出现下面的 “循环论证”:如果希望有满意的输出信号,就需要有满意的输入信号;但由于输入信号直接依赖于对参数或结构的估计值,因此就需要有满意的在线估计值。进一步,由于估计值又依赖于输出信号,从而需要有满意的输出信号,这又回到了论证的起点!这是理论研究中出现困难的基本原因。正因为如此,从理论上建立自适应控制系统的全局稳定性与收敛性等,被认为是这一领域的中心问题,并引起国际控制界的极大关注与广泛研究,成为现代控制理论发展史上的一个绚丽篇章。
本课程将以基于最小二乘的自校正调节器为典型代表,介绍自适应控制的基本特点、难点和成果。具体内容包括:最小二乘自校正调节器的稳定性与最优性问题以及反馈机制的最大能力与局限研究。
L.Guo and H.F.Chen,“The Astrom-Wittenmark self-tuning regulator revisited and ELS based adaptive trackers”, IEEE Trans. Automatic Control, Vol.36, No.7, July, 1991, pp.802-812 .
H.F.Chen and L.Guo, Identification and Stochastic Adaptive Control, Birkhauser,Boston,1991v
L.Guo,“Convergence and logarithm laws of self-tuning regulators”, Automatica, Vol.31, No.3, pp.435–450, 1995
T. E. Duncan , L. Guo and B. Pasik-Duncan, “Adaptive continuous-time linear quadratic gaussian control”, IEEE Trans. Automatic Control, Vol.44, No.9, pp.1653-1662, September, 1999.
郭雷, 回溯自校正调节器研究之路, 系统科学与数学, 32(12),1460-1471,2012.
郭雷, 不确定性动态系统的估计、控制与博弈, 中国科学 : 信息科学 2020 年 第 50 卷 第 9 期 : 1327–1344
L. Guo, “On critical stability of discrete-time adaptive nonlinear control”, IEEE Trans. Automatic Control, Vol.42, No.11, pp.1488-1499, 1997.
C. Li and J. Lam, “Stabilization of discrete-time nonlinear uncertain systems by feedback based on LS algorithm,” SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, vol. 51, no. 2, pp. 1128–1151, 2013.
Z. Liu and C. Li, “Is it possible to stabilize discrete-time parameterized uncertain systems growing exponentially fast?” SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, vol. 57, no. 3, pp. 1965–1984, 2019.
C. Zhao and L. Guo. PID controller design for second order nonlinear uncertain systems, Science China Information Sciences, 60(2), 1-13, 2017. J. Zhang and L. Guo. Theory and design of PID controller for nonlinear uncertain systems, IEEE Control Systems Letters, 3(3), pp.643 - 648, 2019. C. Zhao and L. Guo. Towards a theoretical foundation of PID control for uncertain nonlinear systems, Automatica, vol. 142:110360, 2022. C. Zhao and S. Yuan. Tracking performance of PID for nonlinear stochastic systems, arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.10537, 2023. C. Zhao and L. Guo. Control of nonlinear uncertain systems by extended PID, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 66(8), 3840-3847, 2021. K.J. Astrom and T. Hagglund. PID controllers: theory, design and tuning. Research Triangle Park, NC: Instrument society of America. 1995. 韩京清, 自抗扰控制技术:估计补偿不确定因素的控制技术. 北京:国防工业出版社,2008.
韩京清.自抗扰控制技术. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2008. Huang Y, Xue W. Active disturbance rejection control: methodology and theoretical analysis. ISA Transactions,2014,53:963-976.
Lennart, L., System Identification: Theory for the User, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1999. Chen, H.F. and L. Guo, Identification and Stochastic Adaptive Control, Birkhauser, Boston, 1991.
Le-Yi Wang, George G. Yin, Ji-Feng Zhang and Yanlong Zhao, System Identification with Quantized Observations, Birkhauser, Boston, 2010. Le-Yi Wang, Ji-Feng Zhang and George G. Yin, System identification using binary sensors, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 48(11): 1892-1907, 2003. Le-Yi Wang and George G. Yin, Asymptotically efficient parameter estimation using quantized output observations, Automatica, 43: 1178-1191, 2007. Jin Guo and Yanlong Zhao, Recursive projection algorithm on FIR system identification with binary-valued observations, Automatica, 49(11): 3396-3401, 2013. Ying Wang, Yanlong Zhao, Ji-Feng Zhang and Jin Guo, A unified identification algorithm of FIR systems based on binary observations with time-varying thresholds, Automatica, 135: 109990, 2022. Lantian Zhang, Yanlong Zhao, Lei Guo, Identification and adaptation with binary-valued observations under non-persistent excitation condition, Automatica, 138: 110158, 2022. Yanlong Zhao, Hang Zhang, Ting Wang and Guolian Kang, System identification under saturated precise or set-valued measurements, Science China Information Sciences, 66: 112204, 2023. Jin Guo, Ji-Feng Zhang and Yanlong Zhao, Adaptive tracking control of a class of first-order systems with binary-valued observations and time-varying thresholds, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 56(12): 2991-2996, 2011. Ting Wang, Min Hu and Yanlong Zhao, Adaptive tracking control of FIR systems under binary-valued observations and recursive projection identification, IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 51(9): 5289-5299, 2021. Yanlong Zhao, Ting Wang and Wenjian Bi, Consensus protocol for multi-agent systems with undirected topologies and binary-valued communications, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 64(1): 206-221, 2019. Ting Wang, Hang Zhang and Yanlong Zhao, Consensus of multi-agent systems under binary-valued measurements and recursive projection algorithm, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 65(6): 2678-2685, 2020. Ting Wang, Wenjian Bi, Yanlong Zhao and Wenchao Xue, Radar target recognition algorithm based on RCS observation sequence: Set-valued identification method, Journal of Systems Science and Complexity, 29(3): 1-16, 2016. Guolian Kang, Wenjian Bi, Hang Zhang, Stanley Pounds, Cheng Cheng, Sanjay Shete, Fei Zou, Yanlong Zhao, Ji-Feng Zhang and Weihua Yue, A robust and powerful set-valued approach to rare variant association analyses of secondary traits in case-control sequencing studies, Genetics, 205(3): 1049-1062, 2017. Shuping Tan, Jin Guo, Yanlong Zhao and Ji-Feng Zhang, Adaptive control with saturation-constrainted observations for drag-free satellites: A set-valued identification approach, Science China Information Sciences, 64: 202202, 2021
T. Vicsek, A. Czirok, E. Jacob, I. Cohen, and O. Shochet, Novel type of phase transition in a system of self-deriven particles, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1995, 75(6): 1226–1229.
G.G. Tang, L. Guo, Convergence of a class of multi-agent systems in probabilistic framework, Journal of Systems Science and Complexity, Vol. 20, No. 2, pp. 173-197, June 2007.
Z. X. Liu and L. Guo, Synchronization of multi-agent systems without connectivity assumption, Automatica, 45(12), 2744-2754, 2009. (Regular paper)
G. Chen, Z. X. Liu, L. Guo, The smallest possible interaction radius for synchronization of self-propelled particles, SIAM Review, 56(3), 449-521, 2014. (Sigest paper)
Z. X. Liu, J. Han, X. M. Hu, The proportion of leaders needed for the expected consensus, Automatica, 47(12), 2697–2703, 2011.
J. Deng, L. Wang, Z. X. Liu*, Attitude synchronization and rigid formation of multiple rigid bodies over proximity networks, 125, 109388, Automatica, 2021.
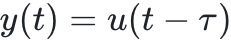 ,其中
,其中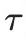 >0为时间延迟, 其传递函数为
>0为时间延迟, 其传递函数为分布参数几乎和现代控制理论同时诞生。1954年钱学森在他的工程控制论的书中就讨论了热传导过程的分布参数系统问题,最早使用了无穷阶传递函数的概念。初期的研究受集中参数系统最优控制的Pontryagin极大值原理的启发,研究各种分布参数系统的最优控制问题。特别是法国数学家J.L.Lions的加入使得分布参数系统最优控制的研究,从泛函分析和偏微分方程的角度系统化, 抽象化。由于无穷的卷入,分布参数系统控制因此成为数学应用最多的控制分支。
本课程分为两个部分:第一部分是分布参数系统的结构理论。包括稳定性、可控性、可观性等。这些概念虽然和集中参数系统目的相同,但由于无穷的问题,很多表达并不完全等同于集中参数系统。第二部分是控制设计问题。给了一个控制问题,无论是集中参数系统还是分布参数系统,控制总要完成一些任务。在控制理论中,所有的控制任务都是通过前馈和反馈实现的。控制论关心的主要是反馈。根本的任务有三条:第一、性能输出要跟踪参考信号;第二、系统要实现内部稳定;第三、系统要抵抗干扰。
在课程里,虽然也讲一些抽象的概念,但我们主要的还是通过例子来说明这一切。
分布参数系统控制,控制理论的若干瓶颈问题,第四章,44-54, 科学出版社,2002年。
郭宝珠、柴树根,无穷维线性系统控制理论,科学出版社,现代数学丛书,2000
第十课:逻辑动态系统的分析与控制
课程简介:
逻辑动态系统指自变量只取有限个值的动态系统,包括2值的经典逻辑(或布尔逻辑)、k值逻辑、(一般)有限值逻辑。上个世纪末,程代展研究员提出了矩阵半张量积,打破了矩阵乘法维数限制的藩篱。近年来,以矩阵半张量积工具,给出了逻辑动态系统的代数状态空间描述方法,其关键点是将逻辑动态系统转化为用矩阵描述的离散时间系统。类似于欧氏空间上由微分或差分方程描述的动态系统的Kalman状态空间方法,它为逻辑动态系统的分析与控制设计提供了一个框架。
本课程将系统介绍基于矩阵半张量积的代数状态空间方法,然后介绍它在逻辑动态系统分析与控制理论上的应用,最后将简略介绍该方法目前在其他更多工程和理论研究领域的应用。
推荐阅读资料:
程代展, 齐洪胜. 矩阵半张量积讲义 卷一: 基本理论与多线性运算, 北京: 科学出版社, 2020.
程代展, 齐洪胜. 矩阵半张量积讲义 卷二: 逻辑动态系统的分析与控制, 北京: 科学出版社, 2022.
程代展, 李长喜, 郝亚琦, 张潇,矩阵半张量积讲义 卷三: 有限博弈的矩阵半张量积方法, 北京: 科学出版社, 2022.
程代展, 纪政平,矩阵半张量积讲义 卷四: 有限与泛维动态系统, 北京: 科学出版社, 2023.
程代展, 冯俊娥, 钟江华, 吴玉虎, 张奎泽,矩阵半张量积讲义 卷五: 工程及其他系统的应用, 北京: 科学出版社, 2024. (即将出版)
课程信息
课程信息
课程目的
课程适用对象
对复杂系统的行为和控制机制感兴趣的跨领域研究者
学习电气工程、机械工程、自动化、计算机科学等工程和科学领域的学生
从事自动化与控制的工程师
对学员基础要求
报名须知
报名须知
一、参与形式
此次系列课程为周更课程,共计 10 节,从2024年4月2日起,每周二晚上7:00-9:00腾讯会议线上上课,三个工作日内上线课程录播。
二、奖学金机制
在集智斑图网站(pattern.swarma.org)完成本课程体系下某个方向的总结文章或学习路径。经集智学园助教团队评定认可后,可作为一条贡献。一条贡献奖励400元奖学金。
可参考:

五、课程咨询
加入VIP,解锁集智课程&读书会
集智长期深耕复杂系统与跨学科研究,在网络科学、系统理论、混沌科学等经典领域持续策划精品课程,同时也追踪因果科学、深度学习、复杂经济学、生命复杂性、社会计算、AI+Science、大模型、神经科学、城市科学等交叉前沿。汇集了大量的探索者,包括教授、硕博、工程师、创业者等等。
为了帮助有学习需求的朋友夯实学科基础,帮有科研需求的朋友深入前沿交流,我们开放了1年制和2年制的集智学园VIP计划。VIP用户可以深度参与集智俱乐部社区,并在会员期内解锁集智学园全站课程权限。

推荐阅读
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢