
导语

Clover青子 | 作者
1. 什么是系统生物学
1. 什么是系统生物学
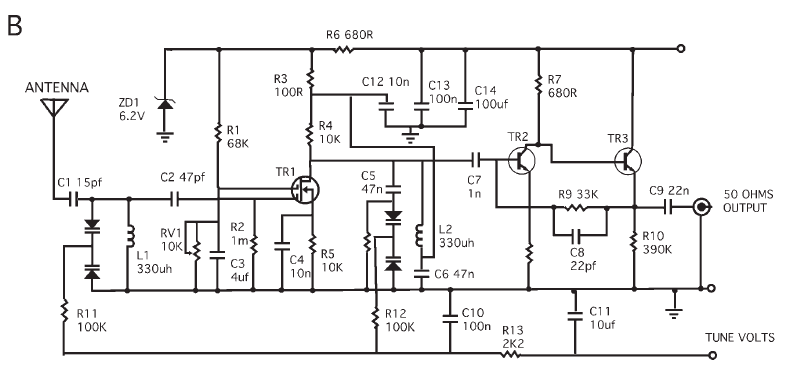
论文题目: Can a biologist fix a radio?—Or, what I learned while studying apoptosis 论文地址: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10541-005-0088-1
论文题目: A whole-cell computational model predicts phenotype from genotype 论文地址: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867412007763
2. 系统生物学的历史进程
2. 系统生物学的历史进程
3. 研究的四个阶段
3. 研究的四个阶段
1. 初步模型 是对选定的某一生物系统的所有组分进行了解和确定,描绘出该系统的结构,包括基因相互作用网络和代谢途径,以及细胞内和细胞间的作用机理,以此构造出一个初步的系统模型。
2. 观测实验
是系统地改变被研究对象的内部组成成分(如基因突变)或外部生长条件,然后观测在这些情况下系统组分或结构所发生的相应变化,包括基因表达、蛋白质表达和相互作用、代谢途径等的变化,并把得到的有关信息进行整合。
3. 分析修订
把通过实验得到的数据与根据模型预测的情况进行比较,并对初始模型进行修订。
4. 理想模型
根据修正后的模型的预测或假设,设定和实施新的改变系统状态的实验,重复第二步和第三步,不断地通过实验数据对模型进行修订和精练。第一到第三阶段,也就是所谓的“整合”- 系统理论、“干涉”- 实验生物学和“信息”- 计算生物学研究过程,即系统生物学通过系统论和实验(Experimental)、计算(Computational)等概念和方法的整合,目标就是要得到一个理想的完整模型,使其理论预测能够全面反映出生物系统的真实性。
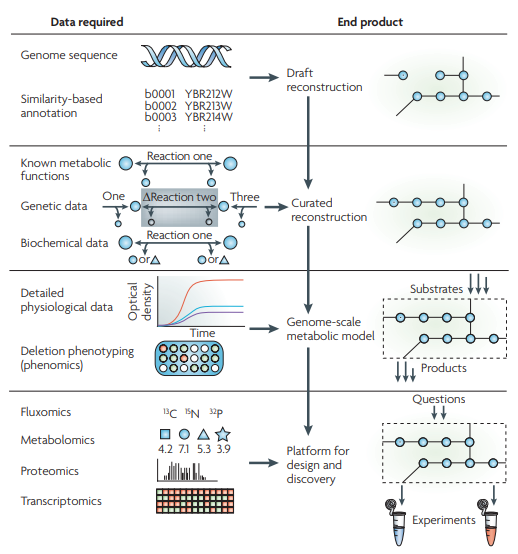
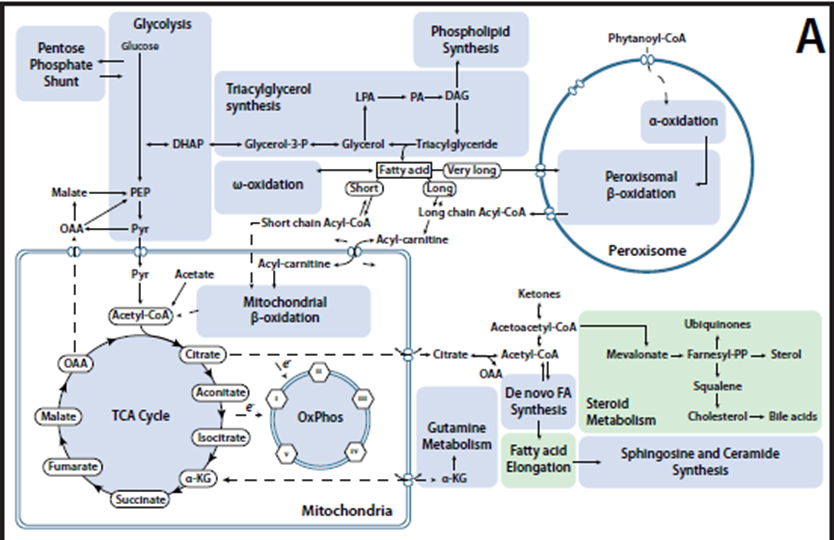
图4:系统生物学重构代谢过程的四个阶段
论文题目: Reconstruction of Biochemical Networks in Microorganisms 论文地址: https://www.nature.com/articles/nrmicro1949
4. 研究方法分类
4. 研究方法分类
“干涉”与“发现”的科学
“干”与“湿”实验
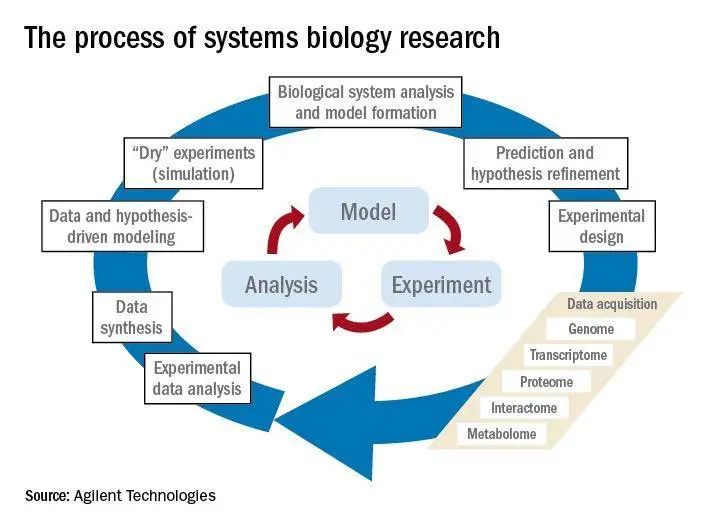
“自顶向下”与“自下而上”的方法
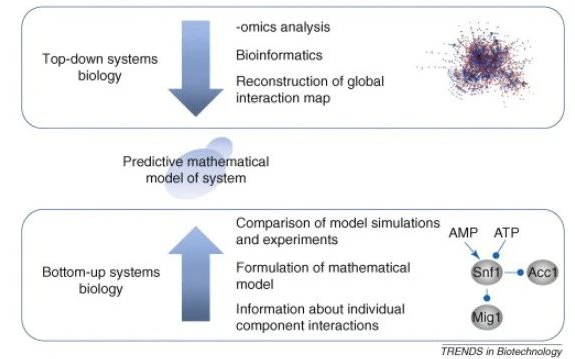
图6:显示不同的系统生物学手段:在自顶向下的系统生物学中,高通量的实验数据,这些数据被用来重建通路或共调控模块。这些模块可以成为更详细的研究的基础,其中单个组件的动力学被量化。在自下而上的系统生物学中,通路的重建是基于对个体成分相互作用的研究。
5. 教材推荐
5. 教材推荐
《系统生物学》
《Systems Biology: Philosophical Foundations》
《Life: An Introduction to Complex Systems Biology》
《Systems Biology: Properties of Reconstructed Networks 》
《An Introduction to Systems Biology: Design Principles of Biological Circuits》


6. 系统生物学经典文献
6. 系统生物学经典文献
贝塔朗菲:一般系统论
论文题目: The Theory of Open Systems in Physics and Biology 论文地址: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/111/2872/23/tab-pdf
论文题目: An Outline of General System Theory (1950) 论文地址: http://www.isnature.org/Events/2009/Summer/r/Bertalanffy1950-GST_Outline_SELECT.pdf
普利高津: 耗散结构理论
论文题目: Thermodynamic Theory of Structure, Stability and Fluctuations. 论文地址: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/bbpc.19720760520
艾根:超循环理论
论文题目: Self organization of matter and the evolution of biological macromolecules 论文地址: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00623322
论文题目: The Hypercycle: A principle of natural self-organization 论文地址: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/qua.560140722
胡德
论文题目: The digital code of DNA 论文地址: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12540920
论文题目: Systems Biology and New Technologies Enable Predictive and Preventative Medicine 论文地址: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:33015388
曾邦哲
北野宏明
论文题目: Computational systems biology 论文地址: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01254
论文标题: The systems biology markup language (SBML): a medium for representation and exchange of biochemical network models 论文地址: https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg015
论文题目: Biological robustness 论文地址: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15520792
专著题目: Synthetic Biology, Volume 1 专著地址: https://www.overdrive.com/media/2502000/synthetic-biology-volume-1
论文题目: Synthetic Biology 论文地址: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrg1637
论文题目: Systems and Synthetic biology: tackling genetic networks and complex diseases 论文地址: https://www.nature.com/articles/hdy200918
生物信息学
论文题目: Digital electronic computers in biomedical science. 论文地址: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14415153
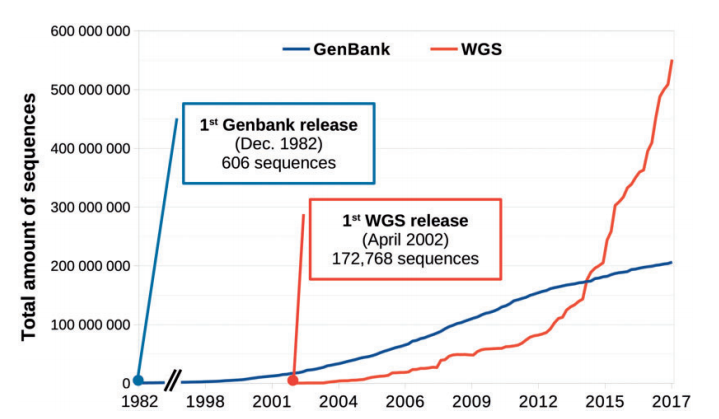
图10:NCBI 基因库和 WGS(Whole Genome Shotgun,全基因组鸟枪法)数据库中随时间变化的序列总数。
Compute Canada (https://www.computecanada.ca)
New York State’s High Performance Computing Program
(https://esd.ny.gov/new-york-state-high-performance
-computingprogram)
The European Technology Platform for High Performance Computing (http://www.etp4hpc.eu/)
China’s National Center for High-Performance Computing (http://www.nchc.org.tw/en/)
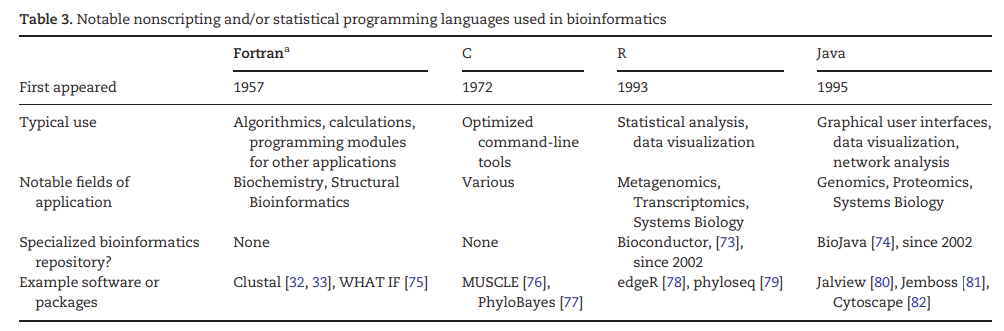
图11:一些生物信息学中使用的非脚本和/或统计编程语言,以及应用软件和程序包[18]。
Science 合集

图12:专题封面图:以模块化闻名的乐高积木,是对生物架构和动态过程一个恰当的比喻,包括从基因表达到组织和有机体的功能各个层次,组件之间的联系、如何被管理的,以及它们是如何进化的。这些都是理解不同层次生物复杂性的关键。
论文题目: Systems Biology: A Brief Overview 论文地址: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/295/5560/1662
论文题目: Reverse Engineering of Biological Complexity 论文地址: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/295/5560/1664
论文题目: A Genomic Regulatory Network for Development 论文地址: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/295/5560/1669
论文题目: Modeling the Heart--from Genes to Cells to the Whole Organ 论文地址: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/295/5560/1678
7. 相关领域前沿文章
7. 相关领域前沿文章
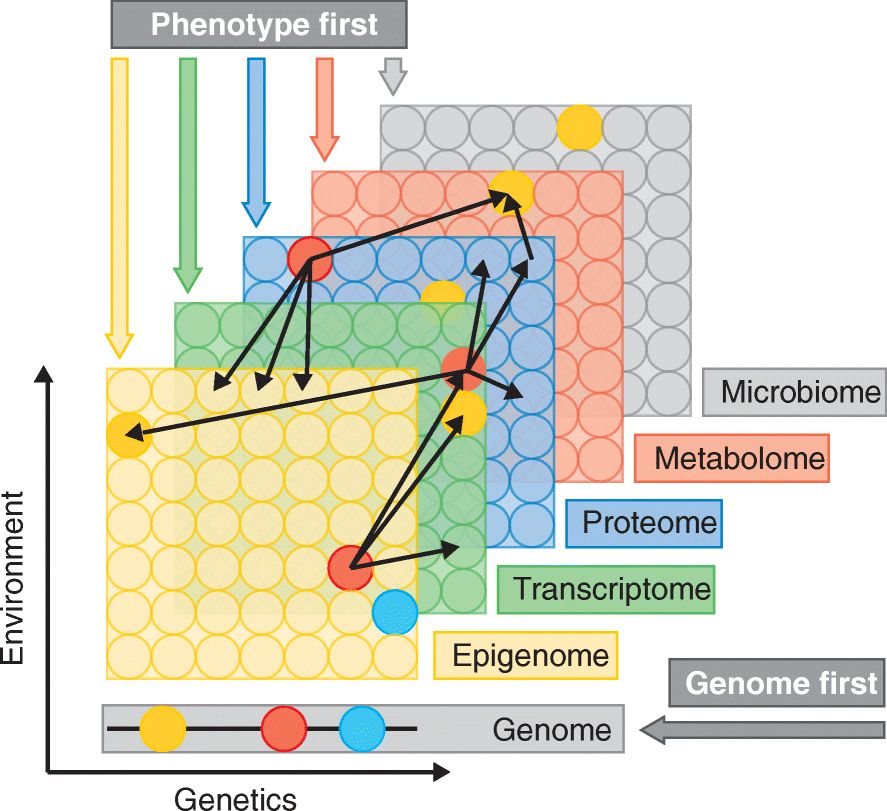
图13:多组学方法对某种特定疾病的研究。组学数据收集在整个分子池上,以圆圈表示。除了基因组外,所有的数据层都同时反映了遗传调控和环境,这可能会对每个个体分子产生不同程度的影响。细黑箭头表示在不同层中检测到的分子之间潜在的相互作用或相关性。例如,红色的转录本可以与多种蛋白质相关联。在同一层中,交互也很普遍,图中未表述[24]。
汉族人全基因组
论文题目: The ChinaMAP analytics of deep whole genome sequences in 10,588 individuals 论文地址: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-0322-9
古DNA组重建人类历史
论文题目: American Association for the Advancement of Science 论文地址: https://www.britannica.com/topic/American-Association-for-the-Advancement-of-Science
泛癌症全基因组(Pan-cancer Genomics)
论文题目: Pan-cancer analysis of whole genomes 论文地址: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-020-1969-6
论文题目: Patterns of somatic structural variation in human cancer genomes 论文地址: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1913-9
论文题目: Analyses of non-coding somatic drivers in 2,658 cancer whole genomes 论文地址: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-1965-x
TCGA数据库
论文题目: Comprehensive Analysis of Genetic Ancestry and Its Molecular Correlates in Cancer, Cancer Genome Atlas Analysis Network 论文地址: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32396860/
癌症信号通路图谱
论文题目: A census of pathway maps in cancer systems biology 论文地址: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-020-0240-7
表观遗传组(Epigenomics)
论文题目: The NIH Common Fund/Roadmap Epigenomics Program: Successes of a comprehensive consortium 论文地址: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw6507
蛋白组 (Proteomics)
论文题目: Human SRMAtlas:A Resource of Targeted Assays to Quantify the Complete Human Proteome 论文地址: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867416308492
论文题目: A reference map of the human binary protein interactome 论文地址: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-020-2188-x
微生物组(Microbiome)
图15:继人类基因组计划之后,美国国立卫生研究院在2007年启动了一个类似的雄心勃勃的计划——人类微生物组计划(Human Microbiome Project,HMP),https://www.hmpdacc.org/。
论文题目: Tackling the Microbiome 论文地址: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/336/6086/1209
论文题目: Extensive Unexplored Human Microbiome Diversity Revealed by Over 150,000 Genomes from Metagenomes Spanning Age, Geography, and Lifestyle 论文地址: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.001
8. 技术与工具
8. 技术与工具
论文题目: A deep learning system accurately classifies primary and metastatic cancers using passenger mutation patterns 论文地址: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-13825-8
论文题目: Software for systems biology: from tools to integrated platforms 论文地址: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3096
参考文献
参考文献可上下滑动查看
本文首发于集智斑图: https://pattern.swarma.org/article/67
本文首发于集智斑图: https://pattern.swarma.org/article/67

扫码阅读路径文章

生命复杂性读书会:
生命复杂系统的构成原理
在生物学中心法则的起点,基因作为生命复杂系统的遗传信息载体,在生命周期内稳定存在;而位于中心法则末端的蛋白质,其组织构成和时空变化的复杂性呈指数式增长。随着分子生物学数十年来的突飞猛进,尤其是生命组学(基因组学、转录组学、蛋白质组学和代谢组学等的集合)等领域的日新月异,当代生命科学临近爆发的边缘。如此海量的数据如何帮助我们揭示宇宙中最复杂的物质系统——“人体”的构成原理和设计原理?阐释人类发育、衰老和重大疾病的发生机制?
集智俱乐部联合西湖大学理学院及交叉科学中心讲席教授汤雷翰,国家蛋白质科学中心(北京)副研究员常乘、李杨,香港浸会大学助理教授唐乾元,北京大学前沿交叉学科研究院研究员林一瀚,中国科学院分子细胞科学卓越创新中心博士后唐诗婕,共同发起「生命复杂性:生命复杂系统的构成原理」读书会,从微观细胞尺度、介观组织器官尺度到宏观人体尺度,梳理生命科学领域中的重要问题及重要数据,由生物学家提问,希望促进统计物理、机器学习方法研究者和生命科学研究者之间的深度交流,建立跨学科合作关系,激发新的研究思路和合作项目。读书会从2024年8月6日开始,每周二晚19:00-21:00进行,持续时间预计10-12周。欢迎对这个生命科学、物理学、计算机科学、复杂系统科学深度交叉的前沿领域感兴趣的朋友加入!

点击“阅读原文”,报名读书会
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除




评论
沙发等你来抢