
导语
当前人工智能领域正在经历一场从“机械执行”到“自主认知”的深刻范式变革,这场变革正在从根本上重塑我们对智能系统的理解、设计和应用方式。随着大模型技术的突破性发展及其在复杂系统建模中的广泛应用,多智能体系统(Multi-Agent Systems, MAS)的研究正经历着前所未有的转型——从传统的基于固定规则的建模(Agent-Based Modeling, ABM)向由LLM驱动的、具备自主认知能力的智能体范式演进。这一转变不仅带来了技术架构的根本性革命,使智能体具备了类人的推理能力、动态适应能力和复杂社交能力,更开创了复杂系统研究的新纪元。
大模型赋能的智能体展现出三大革命性特征:认知深度(能够进行类人的推理和决策,甚至展现出记忆、学习和个性特征)、动态交互(基于自然语言的自主协商和社交行为)以及涌现行为(微观交互产生更复杂的宏观社会现象)。这些特性使得我们可以构建前所未有的"高保真社会模拟器",为理解经济、社会、管理、军事等复杂系统提供了全新视角。


读书会背景
读书会背景
过去几十年里,社会科学家和相关领域的研究者,一直致力于通过实证数据与模型揭示人类行为和智能社会运行的基本规律,试图找出隐藏在各种社会现象和治理痛点背后的因果机制,从而回答“是什么”、“为什么”、“如何治”等一系列问题。Agent建模与仿真作为一种科学方法论在上世纪八九十年代被提出。其核心思想是借助于计算机平台,在一个人工搭建的虚拟环境中创建若干彼此之间以及与环境之间能够交互的Agent,对现实个体行为与环境进行精细刻画,进而辅助研究者的直觉推理。
科学家们围绕经济学等社会科学及工程领域广泛存在的复杂系统和复杂现象所开展的探索工作,如Joshua Epstein 等开发的糖域模型、Brain Arthur 领导开发的人工股票市场模型、Thomas Schelling 的居住隔离模型、Christopher Langton 的人工生命模型都是在这一时期提出和发展起来的。
读书会介绍
读书会介绍
伴随着ChatGPT、DeepSeek这样的大语言模型的兴起,Agent建模与仿真的能力迎来重大跃升。我们不仅可以实现从微观个体行动到宏观群体行为与决策效应/模式的低成本、高可控的探索性模拟研究,揭示复杂系统的非线性、动态性和不确定性等重要特征。还可以通过观察它们合作、竞争、学习、自我修正的行为,加深对大模型的理解,为其策略和动机建立可解释机制,抵御可能的安全、伦理等不可逆风险。
在这八周左右的时间里,山东工商学院副教授高德华、天津大学教授薛霄、北京师范大学教授张江、国防科技大学博士研究生曾利带领大家通过经典、前沿文献领读,带你一起学习与追问。
核心问题
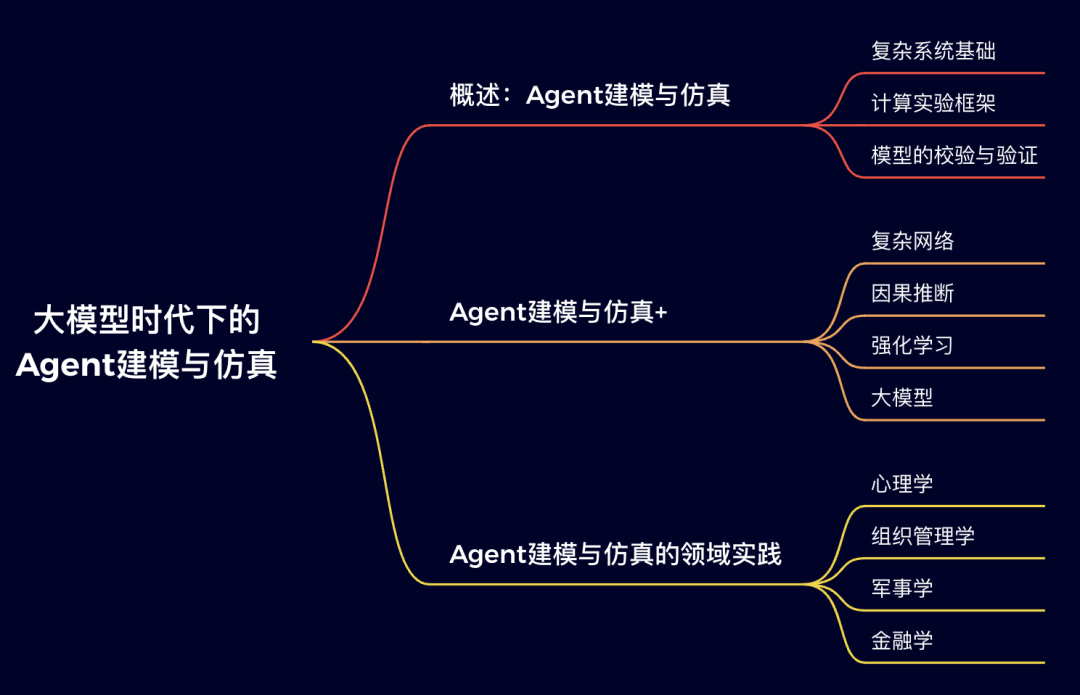
读书会框架
读书会框架
发起人团队
发起人团队

高德华,山东工商学院管理科学与工程学院副教授,管理学博士,硕士生导师。中国仿真学会离散系统仿真专业委员会会员、欧洲组织研究学会(EGOS)会员、亚洲社会仿真学会(ASSA)创始会员兼副秘书长。以第一/通讯作者先后在《公共管理学报》、《系统科学学报》、《Computational and Mathematical Organization Theory》、《Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation》等国内外学术期刊和学术会议上公开发表论文30多篇,参与编撰《Oxford Handbook of Agent-based Computational Management Science》(2024)和《Cambridge Handbook of Routine Dynamics》(2021)两部Handbook,主持完成山东省自然科学基金项目2项,参与国家自然科学基金和国家社会科学基金等多项科研课题。
研究方向:计算组织科学、复杂组织决策与智能管理、工业系统工程。

薛霄,天津大学智能与计算学部,教授、博导。先后获得第八届杨嘉墀科技奖,2023年度IFAC 社会计算杰出成就奖,2023年 CCF服务计算杰出成就奖,省科技创新杰出青年(省杰青), 省高校科技创新人才,省高校青年骨干教师,省学术带头人等荣誉称号。目前兼任:天津市健康人居环境与智慧技术重点实验室副主任;中国自动化学会计算社会与社会智能专委会副主任;IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles 编委;International Journal of Crowd Science 编委;Complex System Modeling and Simulation青年编委。 近年来,主持与参与科研项目包括国家重点研发、国防特区创新、国家自然基金重点、国家自然基金面上、省级重大课题30多项;以第一作者或通信作者在IEEE Trans等顶级期刊与会议上发表论文60多篇,并获得ICWS 2020最佳论文奖(服务计算Top 1会议);2021年计算机研究与发展 Top10 高被引论文;出版著作《复杂系统的计算实验方法》,是国内第一本对计算实验方法进行系统化梳理的专著;获2023年度IFAC TC Award for Outstanding Achievement in Social Computing and CPSS。获省自然科学二等奖2项(均排名第一)、省决策成果二等奖1项(排名第一)、省优秀学术著作一等奖1项(独著)。
研究方向:主要研究方向为服务计算、计算实验、AI Agent、群体智能。

张江,北京师范大学系统科学学院教授,集智俱乐部、集智学园创始人,集智科学研究中心理事长,曾任腾讯研究院、华为战略研究院等特聘顾问。
研究方向:因果涌现、复杂系统分析与建模、规模理论等。

曾利,国防科技大学系统工程在读博士生。
研究方向:研究方向为强化学习、组合优化、复杂网络。
报名参与读书会
报名参与读书会
运行模式
从2025年7月8日开始,每周二晚 19:30-21:30,持续时间预计8周左右,按读书会框架设计,每周进行线上会议,与主讲人等社区成员当面交流,会后可以获得视频回放持续学习。
报名方式
第一步:微信扫码填写报名信息。

扫码报名(可开发票)
第二步:填写信息后,付费报名。如需用支付宝支付,请在PC端进入读书会页面报名支付:https://pattern.swarma.org/study_group/64
第三步:添加运营负责人微信,拉入对应主题的读书会社区(微信群)。
PS:为确保专业性和讨论的聚焦,本读书会谢绝脱离读书会主题和复杂科学问题本身的空泛的哲学和思辨式讨论;如果出现讨论内容不符合要求、经提醒无效者,会被移除群聊并对未参与部分退费。
加入社区后可以获得的资源:
完整权限,包括线上问答、录播回看、资料共享、社群交流、信息同步、共创任务获取积分等。

参与共创任务获取积分,共建学术社区:
读书会采用共学共研机制,成员通过内容共创获积分(字幕修改、读书会笔记、论文速递、公众号文章、集智百科、论文解读等共创任务),积分符合条件即可退费。发起人和主讲人同样遵循此机制,无额外金钱激励。

PS:具体参与方式可以加入读书会后查看对应的共创任务列表,领取任务,与运营负责人沟通详情,上述规则的最终解释权归集智俱乐部所有。
读书会阅读材料
读书会阅读材料
阅读材料较长,为了更好的阅读体验,建议您前往集智斑图沉浸式阅读,并可收藏感兴趣的论文。

https://pattern.swarma.org/article/352?from=wechat
读书会阅读清单
Ageng建模与仿真概述
Elsenbroich, C., & Polhill, J. G. (2023). Agent-based modelling as a method for prediction in complex social systems. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 26(2), 133–142.
An, L., Grimm, V., Sullivan, A., Turner II, B. L., Malleson, N., et al. (2021). Challenges, tasks, and opportunities in modeling agent-based complex systems. Ecological Modelling, 457, 109685.
Stefan Thurner, Rudolf Hanel, and Peter Klimek. Introduction to the Theory of Complex Systems. Oxford University Press, 2018
Gagliolo, M. (2017). Simulate this! An Introduction to agent-based models and their power to iImprove your research practice. International Review of Social Psychology, 30(1)
Macal, C. M. (2016). Everything you need to know about agent-based modelling and simulation. Journal of Simulation, 10(2), 144–156.
Smaldino, P. E., Calanchini, J., & Pickett, C. L. (2015). Theory development with agent-based models. Organizational Psychology Review, 5(4), 300–317.
John H. Miller. Complex Adaptive Systems : An Introduction to Computational Models of Social Life. Princeton University Press, 2011
Bonabeau, E. (2002). Agent-based modeling: Methods and techniques for simulating human systems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99(suppl 3), 7280–7287.
计算实验方法框架
薛霄, 于湘凝, 周德雨, 彭超, 王晓, 周长兵, 王飞跃. 计算实验方法的溯源、现状与展望, 自动化学报, 2023, 49(2): 246-271.
Xiao Xue, Deyu Zhou, Xiangning Yu, Gang Wang, Juanjuan Li, Xia Xie, Lizhen Cui, Fei-Yue Wang. Computational Experiments for Complex Social Systems: Experiment Design and Generative Explanation, IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(4):1022-1038.
盛昭瀚, 张维. 管理科学研究中的计算实验方法[J]. 管理科学学报, 2011,14(05):1-10
模型的校验与验证
Berger, U., Bell, A., Barton, C. M., Chappin, E., Dreßler, G., et al. (2024). Towards reusable building blocks for agent-based modelling and theory development. Environmental Modelling & Software, 175, 106003.
Min Lu, Shizhan Chen, Xiao Xue, Xiao Wang, Yufang Zhang, Feiyue Wang. Computational Experiments for Complex Social System Part II: the Evaluation of Computational Model, IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2022, 9(4): 1224-1236.
Istrate, G. (2021). Models We Can Trust: Toward a Systematic Discipline of (Agent-Based) Model Interpretation and Validation. Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and MultiAgent Systems.
Sargent, R. G. (2020). Verification And Validation Of Simulation Models: An Advanced Tutorial. 2020 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), 16–29.
Lux, T., & Zwinkels, R. C. J. (2018). Empirical Validation of Agent-Based Models. In C. Hommes & B. LeBaron (Eds.), Handbook of Computational Economics (Vol. 4, pp. 437–488). Elsevier.
Donkin, E., Dennis, P., Ustalakov, A., Warren, J., & Clare, A. (2017). Replicating complex agent based models, a formidable task. Environmental Modelling & Software, 92, 142–151.
Galán, J. M., Izquierdo, L. R., Izquierdo, S. S., Santos, J. I., del Olmo, R., et al. (2013). Checking Simulations: Detecting and Avoiding Errors and Artefacts. In B. Edmonds & R. Meyer (Eds.), Simulating Social Complexity: A Handbook (pp. 95–116). Springer.
Sargent, R. G. (2013). Verification and validation of simulation models. Journal of Simulation, 7(1), 12–24.
Midgley, D., Marks, R., & Kunchamwar, D. (2007). Building and assurance of agent-based models: An example and challenge to the field. Journal of Business Research, 60(8), 884–893.
Bianchi, C., Cirillo, P., Gallegati, M., & Vagliasindi, P. A. (2007). Validating and Calibrating Agent-Based Models: A Case Study. Computational Economics, 30(3), 245–264.
Wilensky, U., & Rand, W. (2007). Making Models Match: Replicating an Agent-Based Model. Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation, 10(4):2. https://www.jasss.org/10/4/2.html
模型的可重复性
Berger, U., Bell, A., Barton, C. M., Chappin, E., Dreßler, G., et al. (2024). Towards reusable building blocks for agent-based modelling and theory development. Environmental Modelling & Software, 175, 106003.
Donkin, E., Dennis, P., Ustalakov, A., Warren, J., & Clare, A. (2017). Replicating complex agent based models, a formidable task. Environmental Modelling & Software, 92, 142–151.
Wilensky, U., & Rand, W. (2007). Making Models Match: Replicating an Agent-Based Model. Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation, 10(4):2. https://www.jasss.org/10/4/2.html
Agent建模与仿真+复杂网络
吴江,社会网络计算,2023,电子工业出版社.
Xiao Xue, Xiangning Yu, Deyu Zhou, Xiao Wang, Chongke Bi, Shufang Wang, Fei-Yue Wang. Computational Experiments for Complex Social Systems: Integrated Design of Experiment System, IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(5):1175-1189.
吴江,社会网络的动态分析与仿真实验:理论与应用,2012,武汉大学出版社.
Agent建模与仿真+强化学习
Brusatin, Simone, et al. "Simulating the economic impact of rationality through reinforcement learning and agent-based modelling." Proceedings of the 5th ACM International Conference on AI in Finance. 2024.
Li, Feixue, et al. "An agent-based learning-embedded model (ABM-learning) for urban land use planning: A case study of residential land growth simulation in Shenzhen, China." Land Use Policy 95 (2020): 104620.
Sert, Egemen, Yaneer Bar-Yam, and Alfredo J. Morales. "Segregation dynamics with reinforcement learning and agent based modeling." Scientific reports 10.1 (2020): 11771.
Zhang, Wei, Andrea Valencia, and Ni-Bin Chang. "Synergistic integration between machine learning and agent-based modeling: A multidisciplinary review." IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 34.5 (2021): 2170-2190. (ML+ABM综述文章)
Bilal, Ahsan, et al. "Meta-thinking in llms via multi-agent reinforcement learning: A survey." arXiv preprint arXiv:2504.14520 (2025). (LLM+MARL)
Surina, Anja, et al. "Algorithm discovery with llms: Evolutionary search meets reinforcement learning." arXiv preprint arXiv:2504.05108 (2025). (LLM+RL 用于算法自动发现 被AlphaEvolve引用的文献)
Zhang, Jiayi, et al. "Aflow: Automating agentic workflow generation." arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.10762 (2024). (顶会文章ICLR2025 RL For LLM Agent 蒙特卡洛数搜索用于智能体工作流优化)
Yamada, Yutaro, et al. "The ai scientist-v2: Workshop-level automated scientific discovery via agentic tree search." arXiv preprint arXiv:2504.08066 (2025).(LLM Agent for Science)
Yu, Haofei, et al. "ResearchTown: Simulator of Human Research Community." arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.17767 (2024).
Schmidgall, Samuel, et al. "Agent laboratory: Using llm agents as research assistants." arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.04227 (2025).
Zhou, Zekun, et al. "From hypothesis to publication: A comprehensive survey of ai-driven research support systems." arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.01424 (2025).(综述文献 LLM Agent 用于自动研究 )
Amine Ferrag, Mohamed, Norbert Tihanyi, and Merouane Debbah. "From LLM Reasoning to Autonomous AI Agents: A Comprehensive Review." arXiv e-prints (2025): arXiv-2504. (Autonomous AI Agents文献综述)
Agent建模与仿真+因果推断

Manzo, G. (2022). Agent-based models and causal inference. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
提出因果ABM(Causal Agent-Based Models)来推导描述复杂潜在行为现象的因果结构。
Valogianni, Konstantina, and Balaji Padmanabhan. "Causal abms: Learning plausible causal models using agent-based modeling." The KDD'22 Workshop on Causal Discovery. PMLR, 2022.
Agent建模与仿真+大模型

Tsvetkova M, Yasseri T, Pescetelli N, et al. A new sociology of humans and machines[J]. Nature Human Behaviour, 2024, 8(10): 1864-1876.
Gao, C., Lan, X., Li, N., Yuan, Y., Ding, J., et al. (2024). Large language models empowered agent-based modeling and simulation: A survey and perspectives. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 11(1), 1–24.
Li, N., Gao, C., Li, M., Li, Y., & Liao, Q. (2023, October 16). EconAgent: Large Language Model-Empowered Agents for Simulating Macroeconomic Activities.
Lu, Y., Aleta, A., Du, C., Shi, L., & Moreno, Y. (2024). LLMs and generative agent-based models for complex systems research. Physics of Life Reviews, 51, 283–293.
Mou, X., Ding, X., He, Q., Wang, L., Liang, J., et al. (2024, December 4). From Individual to Society: A Survey on Social Simulation Driven by Large Language Model-based Agents. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2412.03563
Zheng, W., & Tang, X. (2025). Simulating Social Network with LLM Agents: An Analysis of Information Propagation and Echo Chambers. In X. Tang, V. N. Huynh, H. Xia, & Q. Bai (Eds.), Knowledge and Systems Sciences (pp. 63–77). Springer Nature.
Xiao Xue, Shufang Wang, Lejun Zhang, Zhiyong Feng, Yaodan Guo. Social Learning Evolution (SLE): Computational Experiment-based Modeling Framework of Social Manufacturing. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(6): 3343-3355.
Deyu Zhou, Xiao Xue, Zhangbin Zhou. SLE2: The improved Social Learning Evolution Model of Cloud Manufacturing Service Ecosystem, DOI=10.1109/TII.2022.3173053, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(12): 9017-9026.
Deyu Zhou, Xiao Xue, Xudong Lu, Yuwei Guo, Peilin Ji, Hongtao Lv, Wei He, Yonghui Xu, Qingzhong Li, Lizhen Cui. A Hierarchical Model for Complex Adaptive System: From Generative Agent to AI Society, ACM Transactions on Autonomous and Adaptive Systems, https://doi.org/10.1145/3686802, 2024.
Xiao Xue, Fang-Yi Chen, De-Yu Zhou, Xiao Wang, Min Lu, Fei-Yue Wang. Computational Experiments for Complex Social Systems Part I: The Customization of Computational Model, IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2022, 9(5): 1330-1344.
Ale Ebrahim Dehkordi, M., Lechner, J., Ghorbani, A., Nikolic, I., Chappin, É., et al. (2023). Using Machine Learning for Agent Specifications in ABM: A Critical Review and Guidelines. Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation, 26(1), 9.
An, L., Grimm, V., Bai, Y., Sullivan, A., Turner, B. L., et al. (2023). Modeling agent decision and behavior in the light of data science and artificial intelligence. Environmental Modelling & Software, 105713.
Lamperti, F., Roventini, A., & Sani, A. (2018). Agent-based model calibration using machine learning surrogates. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 90, 366–389.
Monti, C., Pangallo, M., De Francisci Morales, G., & Bonchi, F. (2023). On learning agent-based models from data. Scientific Reports, 13(1)
Zhang, W., Valencia, A., & Chang, N.-B. (2023). Synergistic Integration Between Machine Learning and Agent-Based Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Review. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 34(5), 2170–2190.
领域实践
金融学
Axtell, R. L., & Farmer, J. D. (2023). Agent-Based Modeling in Economics and Finance: Past, Present, and Future. Journal of Economic Literature. https://doi.org/10.1257/jel.20221319
Bertani, F., Ponta, L., Raberto, M., Teglio, A., & Cincotti, S. (2021). The complexity of the intangible digital economy: An agent-based model. Journal of Business Research, 129, 527–540.
Farmer, J. D., & Foley, D. (2009). The economy needs agent-based modelling. Nature, 460(7256), 685–686.
Tesfatsion, L. (2023). Agent-Based Computational Economics: Overview and Brief History. In R. Venkatachalam (Ed.), Artificial Intelligence, Learning and Computation in Economics and Finance (pp. 41–58). Springer International Publishing.
组织与管理科学
Blanco-Fernández, D., Leitner, S., & Rausch, A. (2025). Interactions between dynamic team composition and coordination: An agent-based modeling approach. Review of Managerial Science, 19, 1–37.
Wu, J., Ohya, T., & Sekiguchi, T. (2024). Applications of agent-based modeling and simulation in organization management: A quarter-century review through bibliometric mapping (1998–2022). Computational and Mathematical Organization Theory, 30, 1–31.
Onggo, B. S., & Foramitti, J. (2021). Agent-Based Modeling and Simulation For Business and Management: A Review and Tutorial. 2021 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), 1–15. 2021 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC).
Choi, T., & Park, S. (2021). Theory building via agent-based modeling in public administration research: Vindications and limitations. International Journal of Public Sector Management, 34(6), 614–629.
Gómez-Cruz, N. A., Loaiza Saa, I., & Ortega Hurtado, F. F. (2017). Agent-based simulation in management and organizational studies: A survey. European Journal of Management and Business Economics, 26(3), 313–328.
Wall, F. (2016). Agent-based modeling in managerial science: An illustrative survey and study. Review of Managerial Science, 10(1), 135–193.
Secchi D, Neumann M. (2016). Agent-Based Simulation of Organizational Behavior: New Frontiers of Social Science Research. Springer.
Fioretti, G. (2013). Agent-Based Simulation Models in Organization Science. Organizational Research Methods, 16(2), 227–242.
Gao, D. (2024). Using agent-based modeling for theory building in organizational routines. In: Chen, S., Wall, F. & Leitner, S. (eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Agent-based Computational Management Science, Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press
军事学
在多智能体游戏环境中评估大语言模型的决策能力至关重要。本文提出的 GAMA (γ)-Bench 框架,通过八大经典博弈场景动态评估 LLM,揭示模型在策略推理与泛化能力上的差异,为理解 LLM 决策智能提供了全新视角。
Huang, Jen-tse, et al. "Competing large language models in multi-agent gaming environments." The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations. 2025.
张洪广, et al."大模型驱动的智能辅助决策原理与典型应用."指挥与控制学报 10.06(2024):661-668.
Wenyue Hua, Lizhou Fan, Lingyao Li, et al. War and Peace (WarAgent): Large Language Model-based Multi-Agent Simulation of World Wars. arXiv:2311.17227, 2024
罗俊仁, et al."智能推演综述:博弈论视角下的战术战役兵棋与战略博弈."系统仿真学报 35.09(2023):1871-1894.doi:10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.23-0300.
夏立平."双层博弈理论视阈下特朗普政府的朝核政策."美国研究 31.06(2017):123-140+8.
心理学
伍海燕, et al. "大语言模型的情感智能及其心理学应用." 科技导报 43.3 (2025): 47-58.
Nature子刊多篇最新文章速递:与大模型交互过程中的心理学
Sharma, Ashish, et al. "Human–AI collaboration enables more empathic conversations in text-based peer-to-peer mental health support." Nature Machine Intelligence 5.1 (2023): 46-57.
Pataranutaporn, Pat, et al. "Influencing human–AI interaction by priming beliefs about AI can increase perceived trustworthiness, empathy and effectiveness." Nature Machine Intelligence 5.10 (2023): 1076-1086.
Steyvers, Mark, et al. "What large language models know and what people think they know." Nature Machine Intelligence (2025): 1-11.
Wang, Angelina, Jamie Morgenstern, and John P. Dickerson. "Large language models that replace human participants can harmfully misportray and flatten identity groups." Nature Machine Intelligence (2025): 1-12.
关于集智俱乐部读书会和举办方
关于集智俱乐部读书会和举办方
集智俱乐部读书会是面向广大科研工作者的系列论文研读活动,其目的是共同深入学习探讨某个科学议题,了解前沿进展,激发科研灵感,促进科研合作,降低科研门槛。
读书会活动始于 2008 年,至今已经有 50 余个主题,内容涵盖复杂系统、人工智能、脑与意识、生命科学、因果科学、高阶网络等。凝聚了众多优秀科研工作者,促进了科研合作发表论文,孵化了许多科研产品。如:2013 年的“深度学习”读书会孕育了彩云天气 APP,2015 年的“集体注意力流”读书会产生了众包书籍《走近2050》,2020年的开始因果科学读书会孕育了全国最大的因果科学社区等。
主办方:集智俱乐部
协办方:集智学园
集智俱乐部成立于 2003 年,是一个从事学术研究、享受科学乐趣的探索者的团体,也是国内最早的研究人工智能、复杂系统的科学社区。它倡导以平等开放的态度、科学实证的精神,进行跨学科的研究与交流,力图搭建一个中国的 “ 没有围墙的研究所 ”。集智科学研究中心(民间非营利企业)是集智俱乐部的运营主体,其使命为:营造跨学科探索小生境,催化复杂性科学新理论。
集智学园成立于2016年,是集智俱乐部孕育的创业团队。集智学园致力于传播复杂性科学、人工智能等前沿知识和新兴技术,促进、推动复杂科学领域的知识探索与生态构建。

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢